Figure 3.
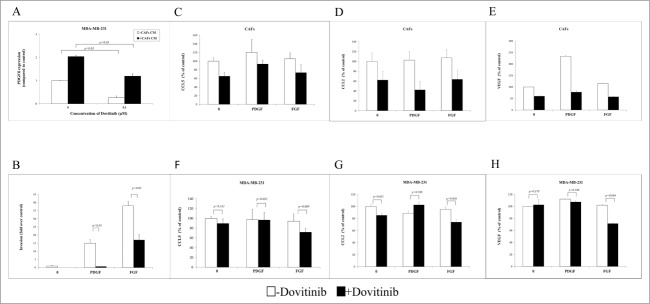
Dovitinib antagonized the PDGF/FGF stimulated MDA-MB-231 cell invasion and chemokine production of CAFs and MDA-MB-231 cells. (A) Dovitinib inhibited the PDGFß expression of MDA-MB-231 cells stimulated with CAFs-conditioned media.CAFs were cultured in serum-free medium for 3 d Cell culture media was collected for further experiment. MDA-MB-231 cells were cultured with serum-free medium or CAFs-conditioned media in the presence of Dovitinib (0.1 μM) for 2 d MDA-MB-231 cells were lysed and PDGFß expression was measured with real-time PCR. Each value presented is the mean ± SD of 3 parallel experiments. (B) Dovitinib antagonized the PDGF/FGF stimulated cell invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells.MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with Dovitinib (0.1 μM) for 2 d Cell invasion assay was performed in serum-free medium, serum-free medium including 10 ng/ml PDGF, or serum-free medium including 10 ng/ml FGF respectively. Each value presented is the mean ± SD of 3 parallel experiments. (C–H) Dovitinib treatment resulted in reduced CCL5, CCL2 and VEGF production in CAFs and MDA-MB-231 cells.CAFs (C-E) or MDA-MB-231 cells (F-H) were treated with PDGF (10 ng/ml) or FGF (10 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of Dovitinib (0.1 μM) for 2 d Cell supernatants were collected; CCL5, CCL2 or VEGF concentration was measured with ELISA.
