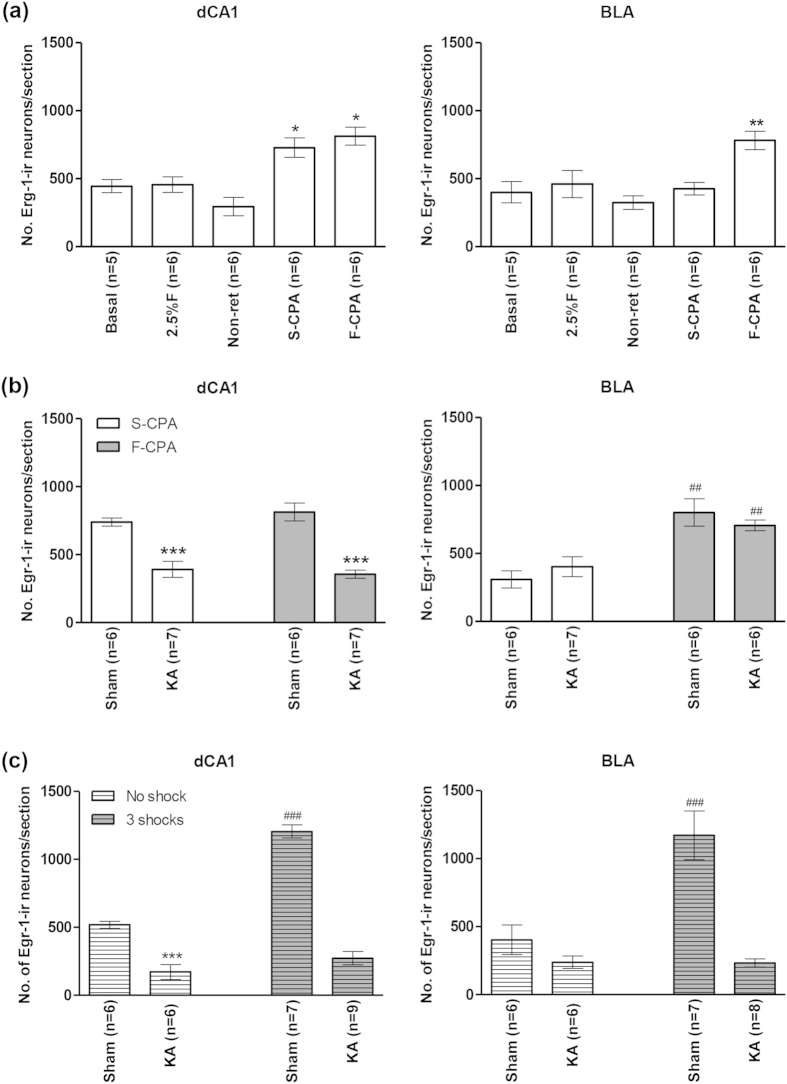
Figure 10. Kainic acid-induced lesion attenuated the contextual fear- but not avoidance-induced expression of Egr-1/Zif268 in basolateral amygdala.
In (a), the effect of conditioning with saline-saline (S-CPA or saline-conditioned place avoidance) or saline-formalin (F-CPA or formalin-conditioned place avoidance) on expression of Egr-1/Zif268-immunoreactivity (ir) was compared vis-à-vis the following groups of animals: home cage (Basal); injected with 2.5% formalin into hind paw and sacrificed 2 h later (2.5% F); conditioned with saline-formalin but without being re-exposed to the training apparatus on the test day (Non-ret). All the animals were Sham animals, that is, they were pre-treated with microinjection of vehicle into the medial septum diagonal band (MSDB). Notice that the number of Egr-1/Zif268-ir neurons were increased in dorsal hippocampus field CA1 (dCA1) to a similar extent in the S-CPA and F-CPA groups of animals. However, in the basolateral amygdala (BLA), the protein was induced only in the F-CPA group. In (b), the effects of conditioning (S-CPA and F-CPA) were compared in kainic acid (KA)-pre-treated animals vs. Sham animals. The neuronal destruction with KA pre-treatment is shown in Fig. 4. The lesion prevented the conditioning-induced expression of Egr-1/Zif268 in dCA1. However, the destruction did not prevent the selective increase of Egr-1/Zif268 in BLA in the F-CPA group. In (c), KA pre-treatment prevented the contextual fear-induced increase of Egr-1/Zif268 in both dCA1 and BLA. Data are mean ± SEM. Statistical significance: ((a) dCA1) *p < 0.05, vs. Basal, 2.5%F and Non-ret; ((a) BLA) **p < 0.01, vs. other groups; ((b) dCA1) ***p < 0.001, vs. Sham S-CPA and Sham F-CPA; ((b) BLA) ##p < 0.01, vs. Sham S-CPA and KA S-CPA; ((c) dCA1) ***p < 0.001 vs. Sham No shock; ###p < 0.001 vs. other groups; ((c) BLA) ###p < 0.0001 vs. other groups. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA.