Figure 4. Microinjection of kainic acid into the medial septal region strongly ablates parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons.
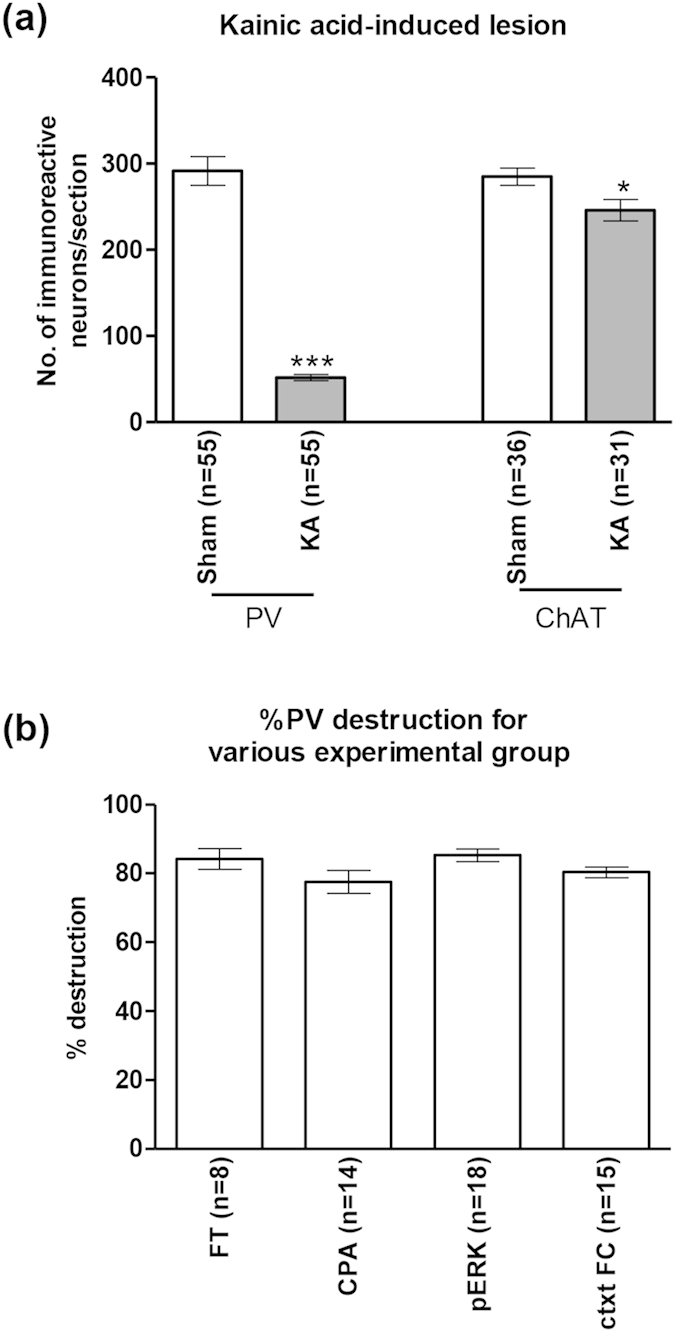
Intraseptal treatment with kainic acid (KA) strongly ablated parvalbumin-immunoreactive (PV-ir) neurons in the septal region with a mild effect on the choline acetyltransferase-immunoreactive (ChAT-ir) neurons (a). Sham animals were pre-treated with vehicle. The ‘n’ values shown on the figure represent the number of animals in each group. On average, 11 sections were used for counting each marker per animal. (b) shows the level of KA-induced destruction of PV-ir neurons in the various experimental groups. The various experimental groups shown are: FT, formalin test; CPA, conditioned place avoidance; pERK, formalin-induced pERK expression in the rACC; ctxtFC, contextual fear conditioning. The ‘n’ values represent the number of animals in each group. Percentage destruction is the number of neurons per section in each KA-treated animal over the average number of neurons per section in the Sham group. Note that the percentage destruction of PV-ir was comparable across the different groups (b). Data are mean ± SEM. Statistical significance: (a) ***p < 0.001 and *p < 0.05 vs. Sham. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired t-test (a) or one-way ANOVA (b).
