Figure 1.
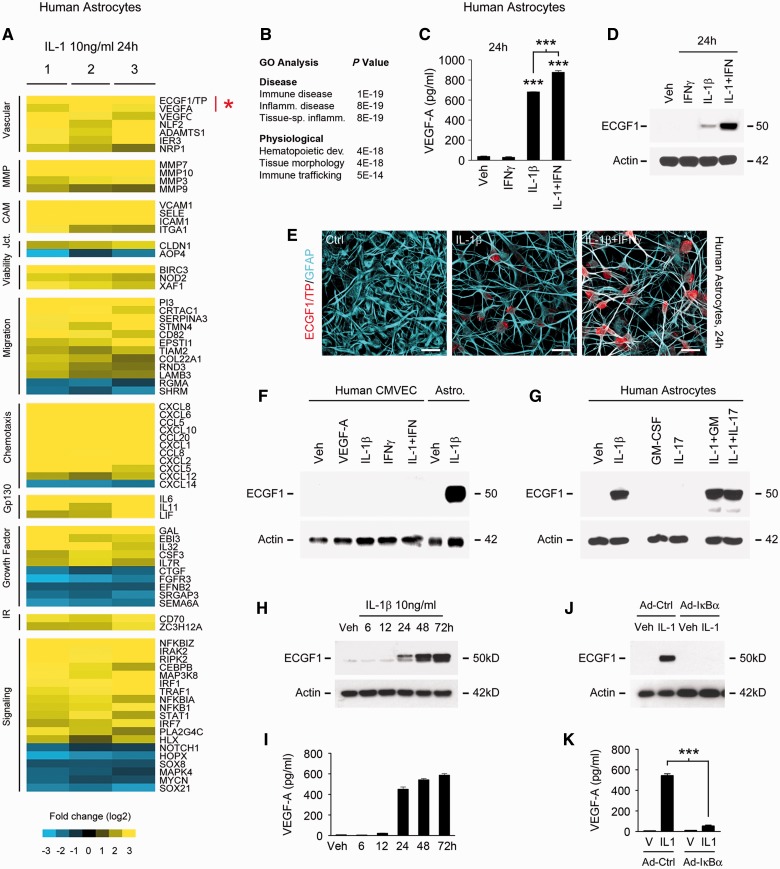
In primary human astrocytes, IL1B induces expression of TYMP, a novel candidate driver of blood–brain barrier disruption. (A) Results of Illumina HumanHT-12 v4 Beadchip© transcriptional profiling of primary human astrocytes treated with IL1B 10 ng/ml for 24 h. Data for three separate cultures screened for purity (as detailed in Supplementary Fig. 1A) are shown, subjected to log2 transformation and colour-coded according to the scale presented below, filtered using Student’s t-test and FDR correction P < 0.05 and sorted using Cluster/Treeview software. TYMP (ECGF1) is among the most strongly induced transcripts (mean FC 10.52) in astrocytes exposed to IL1B, comparable in magnitude to that of the blood–brain barrier permeability factor VEGFA. Other molecules downstream of IL1B include upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases, CXC/CC chemokines, and adhesion molecules, all implicated in blood–brain barrier permeability. (B) GO analysis of data shown in A using Ingenuity© software reveals that functional pathways downstream of IL1B include immunologic and inflammatory disease, and immune cell trafficking. (C and D) Sandwich ELISA (C) and immunoblotting (D) demonstrate that VEGFA and TYMP are both induced by IL1B at 24 h and that induction is potentiated by IFNG, which in isolation is not sufficient for these effects. (E) Immunocytochemistry confirms that TYMP protein is induced in the cytoplasm of human astrocytes exposed to IL1B, and more strongly by IL1B + IFNG in combination. (F and G) Immunoblotting of human cultures demonstrates that TYMP induction by IL1B + IFNG is astrocyte-specific. (F) TYMP is not induced in CMVEC by these cytokines or 100 ng/ml VEGFA. (G) Astrocytic TYMP induction does not occur in response to other inflammatory cytokines such as CSF2 (GM-CSF) or IL17, nor is it potentiated by the addition of these factors to IL1B. (H and I) Both astrocytic TYMP and VEGFA induction in response to 10 ng/ml IL1B are first observed at 24 h and peak at 48 h, and persist at 72 h. (J and K) Blocking activity of the IL1B-activated transcription factor NFκB1 using an adenoviral IκBα super-repressor prevents induction of both TYMP and VEGFA in primary human astrocytes. See also Supplementary Fig. 1B. Results in all panels are representative of three independent experiments in separate cultures. Statistics: A = t-test plus FDR correction; C and K = ANOVA plus Bonferroni test. Scale bars in E = 10 μm.