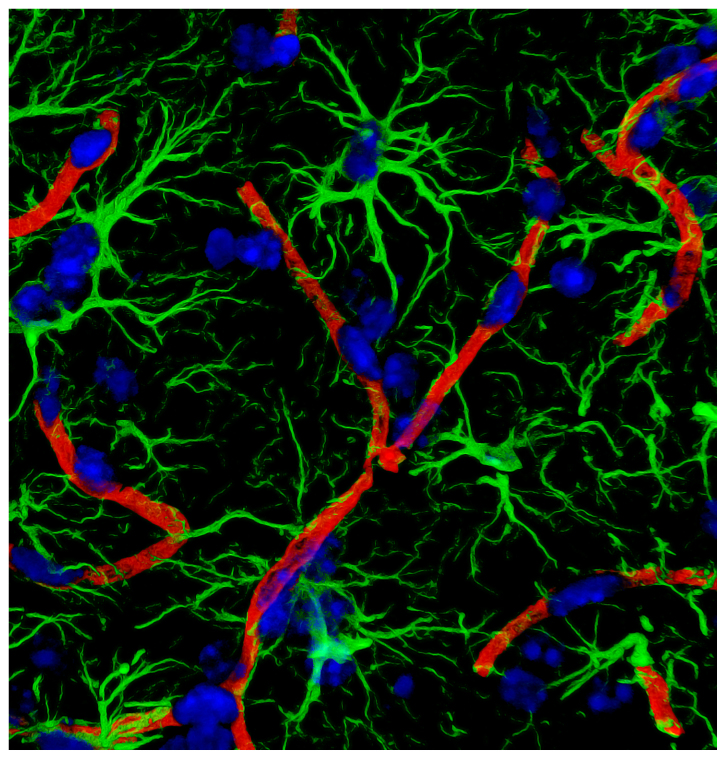
Reactive astrocytes promote breakdown of the blood-brain barrier in multiple sclerosis. Chapouly et al. demonstrate that astrocyte-derived VEGF-A and DDR, the enzymatic product of a newly recognised astrocyte-derived protein, endothelial cell growth factor-1/thymidine phosphorylase (ECGF1/TP), synergistically drive blood-brain barrier permeability in inflammatory brain lesions.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.