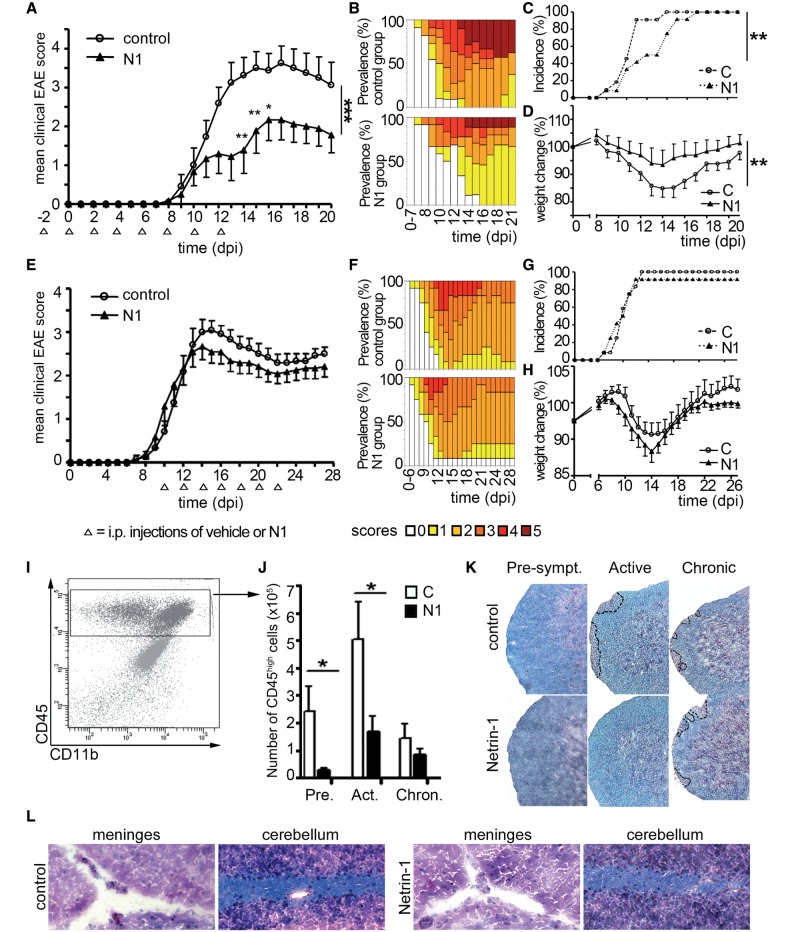
Figure 5.
Netrin 1 reduces severity of EAE. Mean cumulative clinical scores (A and E), score prevalence per treatment group (B and F), disease incidence (C and G) and weight change (D and H) were recorded from MOG35-55-immunized C57BL/6 mice injected intraperitoneally with vehicle control (C) or recombinant netrin 1 (N1). Treatment (open arrowheads) was initiated either before disease induction (A–D) or at the onset of symptoms (E–H). Data shown are representative of n = 3 independent experiments for the prophylactic regimen (A–D; n = 44 animals per group) and of n = 2 independent experiments for the therapeutic regimen (E–H, n = 24 animals per group). CNS infiltrating leucocytes (CD45high population (I) were quantified by flow cytometry (J) in the preclinical (Pre; Day 8), active (Act; Day 13) and chronic (Chron; Day 20 post-induction) phase of EAE, in controls animals and in animals treated prophylactically with netrin 1. Data shown are the mean ± SEM of n = 12 animals per group (selected to be representative of the mean score of the group, at sacrifice), from three independent experiments. Luxol Fast blue/haematoxylin and eosin (LHE) stainings (K) of spinal cord sections of control and netrin 1-treated animals in the preclinical (Pre), active (Act) and chronic (Chron) phase of EAE. Areas of immune cell infiltration are shown with dotted lines. LHE staining of brain sections (L) from control (left) and netrin 1-treated (right) animals in the active phase of EAE. Data shown are representative of n = 12 sections, from four animals per group, and from n = 3 independent experiments. (*P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01).