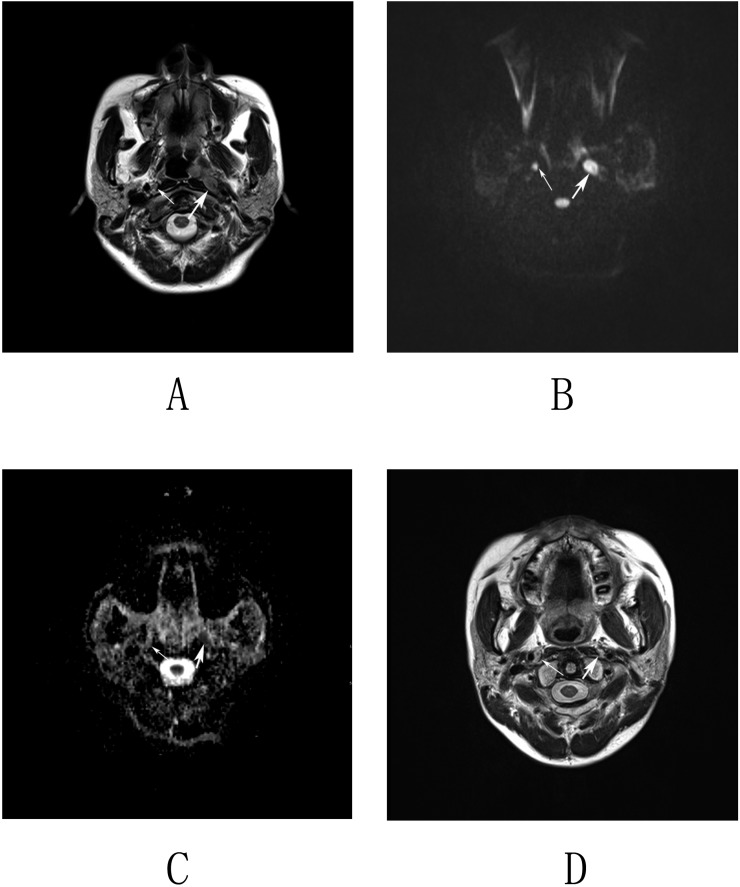
Figure 2.
Imaging by MRI and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a 48-year-old male. (a) Axial T2 weighted images revealed an enlarged lymph node in the left retropharyngeal space (thick arrow) and a lymph node with the short-axis diameter of 5 mm in the right retropharyngeal space (thin arrow). (b, c) Corresponding DWI and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map. The left lymph node displays a high homogeneous signal intensity on the DWI map and a low homogeneous signal intensity on the ADC map (thick arrows). The right lymph node displays a slightly high but homogeneous signal intensity on both the DWI and ADC maps (thin arrows). The mean and minimum ADC values of the left retropharyngeal lymph nodes (RLNs) were 0.899 × 10−3 and 0.813 × 10−3 mm2 s−1. The mean and minimum ADC values of the right RLN were 1.312 × 10−3 and 1.21 × 10−3 mm2 s−1, respectively. (d) Axial T2 weighted images obtained at 12 months following radiation therapy show that the left lymph node was resolved, whereas the right lymph node remained stable.