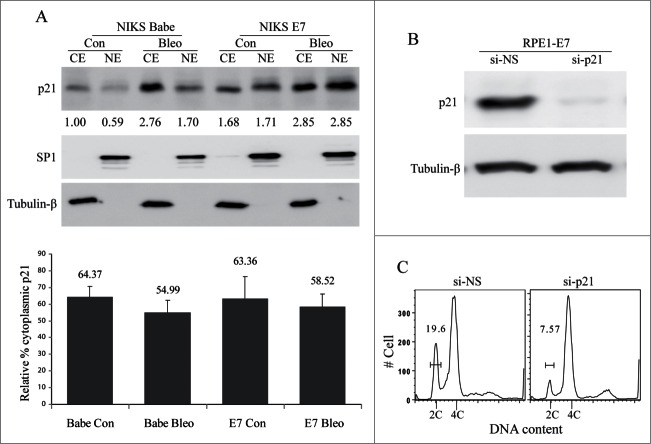
Figure 4.
Role of p21 in E7-mediated S-phase entry. (A) The cellular localization of p21 in E7-expressing cells. NIKS cells expressing HPV-16 E7 or vector (Babe) were treated with bleomycin or PBS, the cytoplasmic protein extract (CE) and nuclear protein extract (NE) were prepared, equal amount of total protein from each fraction were loaded to SDS-PAGE and blotted with antibodies specific for p21, SP1 (Nuclear protein marker) and tubulin-β (Cytoplasmic protein marker). Data from a representative experiment of 3 are shown. Relative amount of p21 based on the normalization with SP1 and Tubulin-β was labeled. Data are summarized in lower panel and described as relative percent of the cytoplasmic p21. (B) siRNAs targeting p21 specifically reduces its expressions. RPE1-E7 cells were transfected with p21-siRNAs and the steady-state level of p21 was monitored by immunoblot analysis. Tubulin-β was used as a loading control. A representative of 2 independent experiments is shown. (C) Role of p21 in E7-mediated abrogation of the G1 checkpoint. RPE1-E7 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting p21, treated with bleomycin, stained with PI and analyzed by flow cytometry. A representative experiment of 2 is shown.