Figure 1.
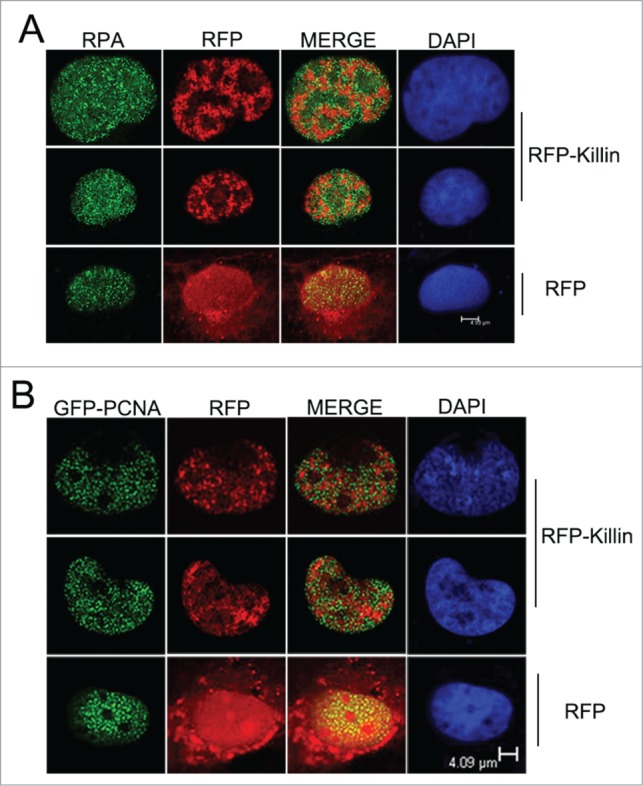
RFP-Killin and DNA replication accessory proteins exhibit mutually exclusive nuclear expression pattern during S-phase. (A) S-phase co-localization of RFP-Killin with RPA. The RFP-Killin in-frame fusion protein or RFP control expression vectors were transiently transfected into Cos-E5 cells. Twenty-four hours after the transfection, S phase cells undergoing DNA replication were visualized by punctate staining with anti-RPA70, followed by secondary Alexa Flour488 goat anti-Rabbit IgG (green). Representative images of the co-localization of RPA and RFP-Killin in the nucleus viewed by confocal microscopy. The two proteins showed a mutually exclusive pattern (merge), in contrast to RPA vs RFP control. The scale bar was at 4.93 μm. (B) S-phase co-localization of RFP-Killin with GFP-PCNA. The RFP-Killin or RFP expression vectors were transiently co-transfected with GFP-PCNA into Cos-E5 cells. The S-phase cells undergoing DNA replication as marked by punctate nuclear GFP-PCNA staining were visualized by confocal microscopy. Representative images of the co-localization of GFP-PCNA and RFP-Killin in the nucleus showed a mutually exclusive pattern (merge), in contrast to RFP control. The scale bar was at 4.09 μm.
