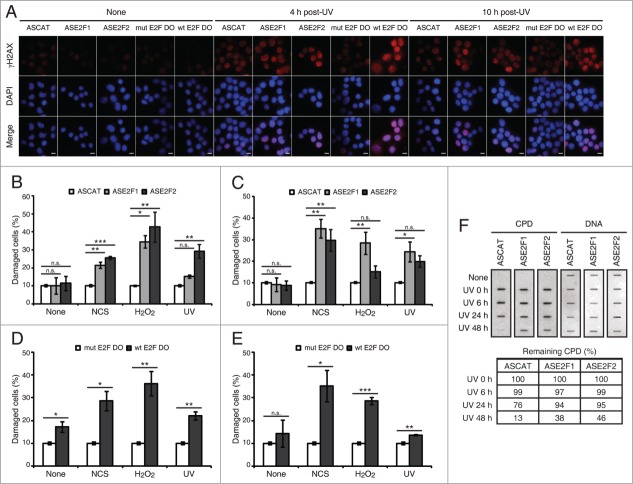
Figure 5.
Blockade of E2F1 and E2F2 induction increases γH2AX intensity and reduces DNA repair capability in response to DNA damage. (A–E) Neuro-2A cells transfected with 1 μM of the indicated ODN, exposed to NCS, H2O2 or UV (A) for 4 h (B and D) or 10 h (C and E), fixed and immunostained using anti-γH2AX antibody. Nuclei were visualized with DAPI staining. Scale bar, 10 μm. In (B–E), data represent the mean±S.E.M. of at least 3 independent experiments, in which 300 to 1000 cells were analyzed for each condition. The percentage of damaged cells was obtained by measurement of γH2AX intensity levels. Quantifications were carried out so that data is expressed relative to the control ODNs ASCAT or mut E2F DO, which represent the 10% of the maximum γH2AX intensity detected. P-values were obtained by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's posttest in (B and C) and Student's t-test in (D and E): *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s. not significant. (F) SH-SY5Y cells transfected with 1 μM of the indicated ODN, UV-irradiated and harvested immediately (0 h) or at 6, 24 or 48 h post-irradiation. Genomic DNA was slot-blotted and analyzed by immunoblot for CPD photoproducts. Methylene Blue staining for total DNA was used as a loading control. The table indicates the average of 2 independent experiments of the percentage of remaining CPD photoproducts, obtained by CPD quantitation and normalization to total DNA. DO, decoy oligodeoxynucleotide.