Figure 2.
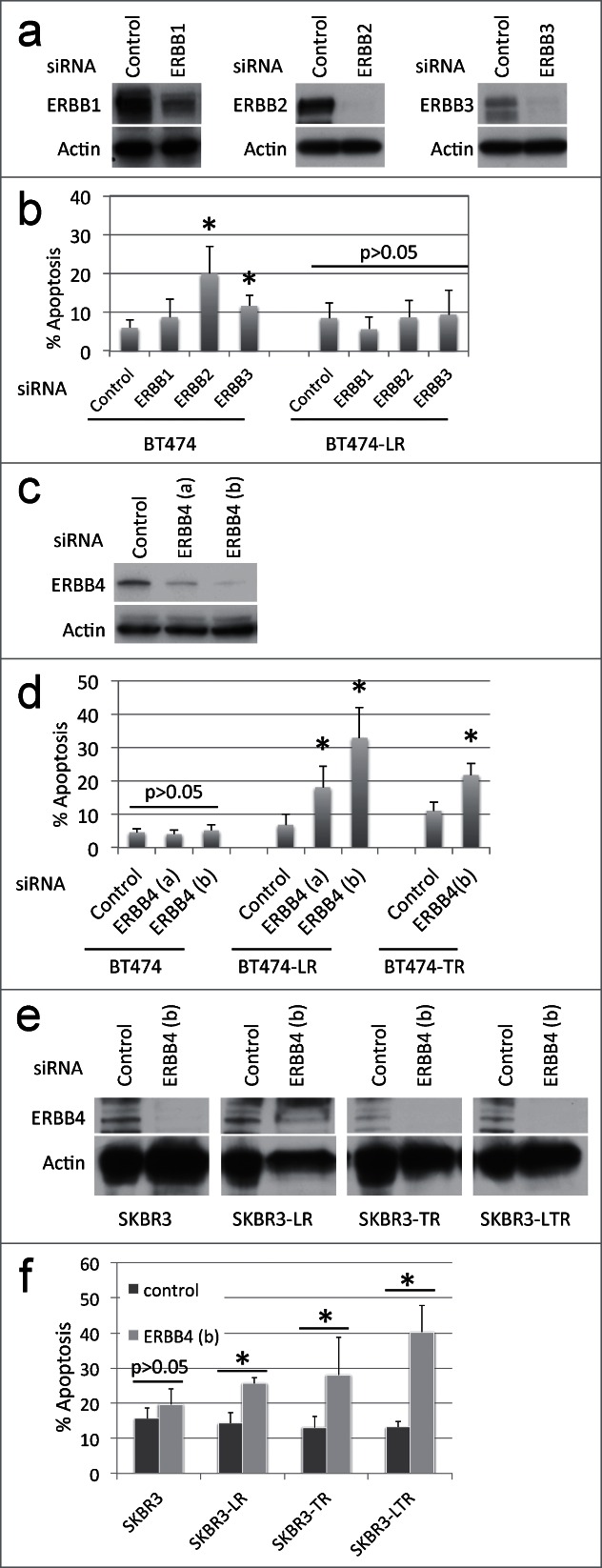
siRNA knockdown of each ERBB member shows that ERBB4 is required for breast cancer cells with acquired resistance to ERBB2+ inhibitors. (a) BT474 and BT474-LR cells were plated at a density of 0.4 × 106 per 6 cm plate. Eighteen hours later, cells were treated with control, EGFR, ERBB2, or ERBB3-specific siRNA (20 nM). After 72 hours, cells were harvested and protein levels of EGFR, ERBB2, ERBB3, and actin were analyzed by western blots. (b) Seventy-2 hours following siRNA knockdown, apoptosis was measured by Annexin-V staining. *P < 0.05 by t-test between control and ERBB2 and between control and ERBB3 (n = 4, error bars indicate SD). (c) BT474 and BT474-LR cells were plated at a density of 0.4 × 106 per 6 cm plate. Eighteen hours later, cells were treated with control or one of 2 ERBB4-specific siRNAs (a) or (b) (10 nM). After 72 hours, cells were harvested and protein levels of ERBB4 and actin were analyzed by protein gel blot. (d) Seventy-2 hours following siRNA knockdown in BT474, BT474-LR (lapatinib resistant), and BT474-TR (trastuzumab resistant), apoptosis was measured by Annexin-V staining. *p < 0.05 by t-test between control and ERBB4 (a) or (b) (n = 4, error bars indicate SD). (e) siRNA knockdown was performed using siRNA ERBB4 (b) in SKBR3, SKBR3-LR (lapatinib resistant), SKBR3-TR (trastuzumab resistant), and SKBR3-LTR (lapatinib and trastuzumab resistant) cells. After 72 hours, cells were harvested and protein levels of ERBB4 and actin were analyzed by western blot. (f) Seventy-2 hours after siRNA knockdown in SKBR3, SKBR3-LR, SKBR3-TR, and SKBR3-LTR, apoptosis was measured by Annexin-V staining. *p < 0.05 by t-test between control and ERBB4 (b) (n = 4, error bars indicate SD). Note that these knockdown experiments were carried out in the absence of lapatinib.
