Figure 1.
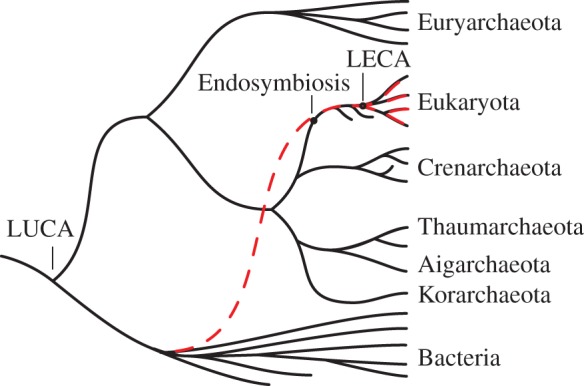
Schematic of the two domains of life. The stem eukaryotes diverged from the archaeal sister group and acquired the shared derived features of eukaryotes, leading to LECA, the last eukaryotic common ancestor and modern eukaryotes. At some point in the eukaryotic stem, bacteria became endosymbiotic and were eventually transformed into mitochondria. The relationship between the acquisition of the defining features of eukaryotes and the timing of the endosymbiosis remains a subject of controversy. Any features of eukaryotes, however, that can be considered sequelae to the endosymbiosis must have evolved subsequent to the acquisition of bacterial symbionts. (Online version in colour.)
