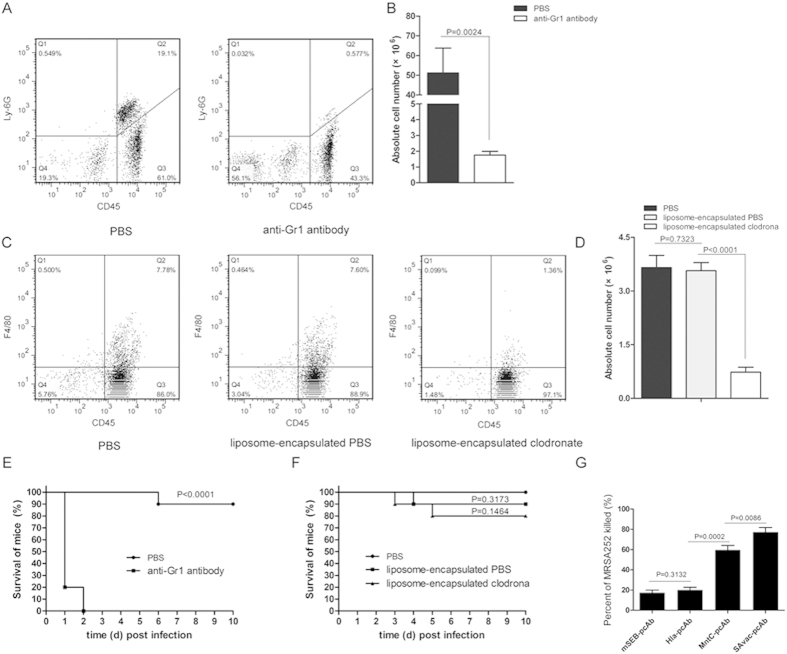
Figure 4. Neutrophils are involved in SAvac-pcAb induced protection against lethal S. aureus challenge.
(A,B) Neutrophils in BALB/c mice (n = 5) were depleted using anti-Gr1 antibody as previously described. Flow cytometry assay indicated that the percentage (A) and absolute number (B) of neutrophils in depleted mice were significantly reduced when compared to PBS-treated group. (C,D) Macrophages in BALB/c mice were depleted with liposome-encapsulated clodronate, flow cytometry assay indicated that percentage (C) and absolute numbers (D) of macrophages in the liposome-encapsulated clodronate group were significantly reduced when compared to liposome-encapsulated PBS, whereas the latter exhibited no difference when compared to PBS controls. (E,F) Survival rates of neutrophil (E) and macrophage (F) depleted or control mice (n = 10) were infected with MRSA252 and passively immunized with SAvac-pcAb. The differences between vaccinated and control mice were presented as p-value. (G) Opsonophagocytic killing assay, MRSA252 was incubated in the presence of isolated 4 × 105 HL-60 cells and pcAb in the presence of infant rabbit complement for 2 h at 37 °C, and plated on agar medium and incubated for 24 h before measuring bacterial survival as determined by CFU. The percentage of killing was calculated to determine killing activity. Data shown were means ± standard deviation (SD) derived from three independent experiments. The differences between each group were presented as p-value.