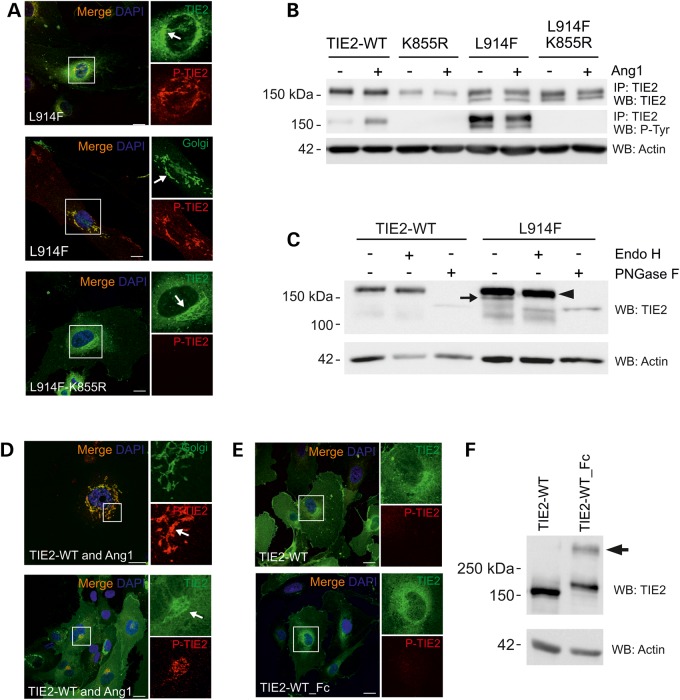
Figure 2.
Incomplete N-linked glycosylation and premature intracellular clustering, but not increased phosphorylation may contribute to Golgi retention of TIE2-L914F. (A) HUVECs were transduced with TIE2-L914F combined with the kinase-inactivating mutation K855R and stained for confocal microscopy. Arrow indicates intensive perinuclear staining in the Golgi. (B) TIE2 was immunoprecipitated and P-Tyr state was analyzed in cell lysates. K855R abrogated mutant TIE2 P-Tyr. Also notice two prominent protein forms in L914F. (C) Cell lysates from transduced HUVECs were undigested, or digested with Endo H or PNGase F and protein migration was analyzed in western blot. Undigested (−) TIE2-L914F migrated as two protein bands, Endo H sensitive form is indicated by an arrow. PNGase F digested both immature (Endo H sensitive) and fully glycosylated forms (arrowhead). (D) HUVECs were co-transduced with TIE2-WT and Ang1 or (E) with TIE2-WT_Fc fusion to induce intracellular receptor clustering and dimerization, respectively, and stained for confocal microscopy. Scale bar 25 µm. (D) Ang1 clustered TIE2 is activated and accumulated in the Golgi. (E) TIE2-WT and TIE2-WT_Fc show some perinuclear TIE2 staining, but no apparent accumulation or P-TIE2 in the Golgi. (F) Non-reduced western blot analysis of TIE2-WT_Fc shows dimeric TIE2 (arrow). IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, western blot.