Figure 1.
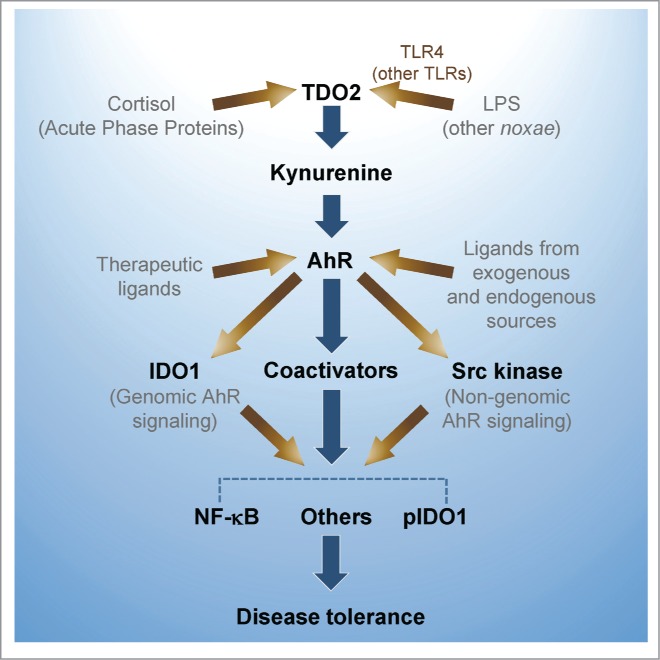
AhR controls hyperinflammatory responses to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and other noxae, and contributes to "disease tolerance." An LPS sublethal dose activates TDO2 leading to kynurenine production from tryptophan. Kynurenine, by acting as an AhR ligand increases IL-10, and decreases IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6. High-dose LPS rechallenge in primed mice triggers IDO1 phosphorylation by AhR complex-associated Src kinase activity and TGF-β production. IDO1 further increases kynurenine production, phosphorylated IDO1 acts a signaling molecule, and AhR, in association with several transcriptional partners, contributes to reprogramming gene expression and chromatin remodeling. LPS-tolerant mice challenged with either gram-negative or gram-positive bacteria are less prone to inflammatory pathology.
