Figure 1.
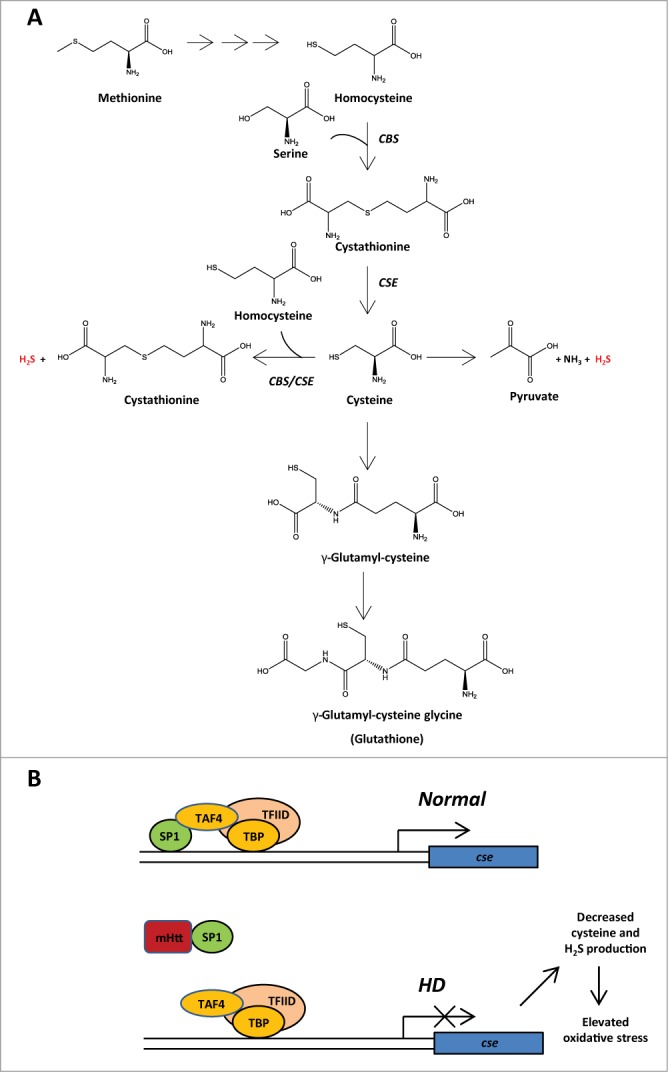
Cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE), the biosynthetic enzyme for cysteine is depleted in Huntington's disease (HD) at the transcriptional level. (A) CSE is a key enzyme in the reverse transsulfuration pathway which generates cysteine from its precursor, cystathionine. Cystathionine is synthesized by cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) by condensing homocysteine derived from dietary methionine with serine. Both CSE and CBS generate the major gasotransmitter hydrogen sulfide (H2S) from cysteine as well as homocysteine. In addition, cysteine serves as a building block for biosynthesis of the antioxidant glutathione. (B) Under normal conditions, CSE transcription is regulated by the transcription factor specificity protein 1 (SP1) in conjunction with associated coactivators such as TATA box binding protein (TBP), TBP-associated factor 4 (TAF4), subunits of the general transcription factor, transcription factor II D (TFIID). In HD, mutant huntingtin (mHtt)sequesters SP1 leading to a diminished expression of CSE, which results in lowered cysteine levels, elevated oxidative stress and neurodegeneration.
