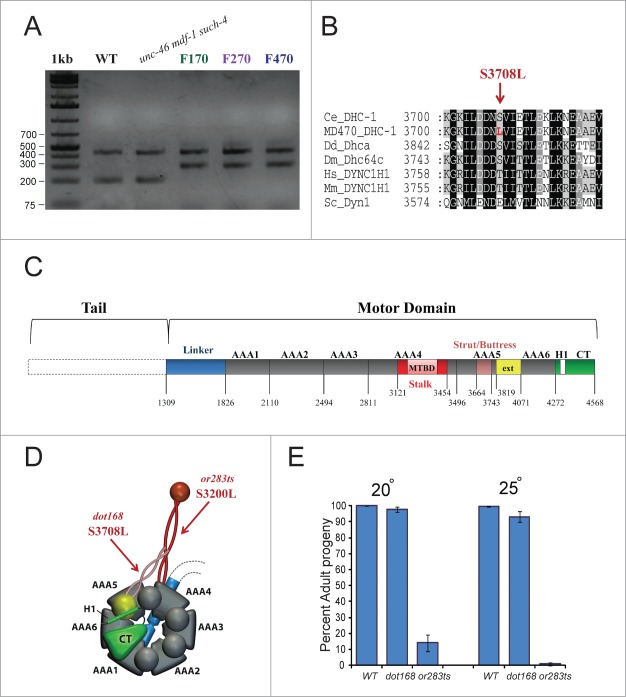
Figure 2.
dhc-1(dot168) suppresses lethality and sterility in the absence of MDF-1. (A) Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR20 analysis of dhc-1(+), unc-46 (e177) mdf-1(gk2) such-4(h2168) and unc-46 (e177) mdf-1(gk2) such-4(h2168); dog-1(gk10) mutation accumulation lines at F170, F270 and F470. The 439 bp product of the 2 outer primers was present in all strains; the 199 bp product of the wild-type allele was present in WT and unc-46 (e177) mdf-1(gk2) such-4(h2168); the 299 bp product of the dhc-1(dot168) mutant allele was present in F170, F270 and F470. (B) dhc-1(dot168) changed serine to leucine at position 3708 within the strut/buttress motif of the fifth AAA ATPase domain. Other organisms also have serine or threonine in this position (or glutamic acid for budding yeast). Organisms: Ce (Caenorhabditis elegans), Dd (Dictyostelium discoideum), Dm (Drosophila melanogaster), Hs (Homo sapiens), Mm (Mus musculus) and Sc (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). (C) Graphic representation of the dynein heavy chain motor domain organization based on the D. discoideum structure.18 We used T-Coffee (http://www.tcoffee.org) to align the C. elegans DHC-1 sequence to D. discoideum Dhca and based on homology extrapolated the location of the important motifs and domains in C. elegans DHC-1. (D) 3D model of the motor domain with arrows pointing to locations of dot168 and or283ts. The model was made based on the previously published model.31 (E) Phenotypic analysis of dhc-1(dot168) and dhc-1(or283ts) at 20°C and 25°C. The graph represents percent of progeny that develop into adults, while error bars represent SEM.