Figure 4.
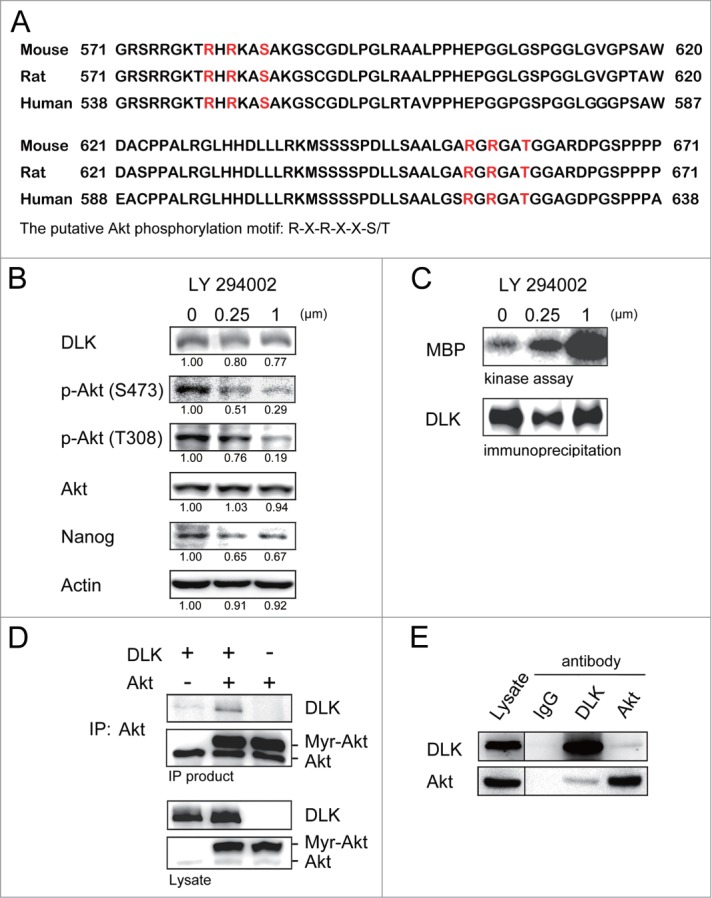
Inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling increases DLK activity in D3 ES cells. (A) DLK has conserved Akt putative phosphorylation sites in mouse, human, and rat. Mouse, rat and human DLK protein sequences were aligned with CLUSTAL 2.0.12 multiple sequence alignment program.58 Two putative Akt phosphorylation sites in C-terminal of mouse DLK protein are located at Serine 584 and Threonine 659. (B) LY-294002 treatment down-regulated Akt activity and expression of Nanog protein. Western blotting was performed to detect DLK, phospho-Akt at S473, phospho-Akt at T308, total Akt, Nanog and actin after D3 mouse ES cells were treated with 0, 0.25 and 1.0 μM of LY-294002. Under the same condition, (C) DLK activity increased does-dependently upon the treatment of LY-294002. Western blotting and kinase assay using MBP as substrates were carried out as DLK protein was immunoprecipitated. (D) DLK interacted with Akt in the overexpression system. Akt immunoprecipitated products from lysates of mouse ES cells overexpressed DLK, Akt, or DLK plus Akt were hybridized with DLK and Akt antibody in Western blotting analysis. (E) The interaction between endogenous DLK and Akt was demonstrated by co-immunoprecipitation assay. After DLK or Akt protein was immunoprecipitated from D3 mouse ES cells, the co-immunoprecipitated proteins were identified by Western blotting and interaction between endogenous DLK and Akt was demonstrated. The rabbit IgG was used as negative control in the experiment.
