Figure 1.
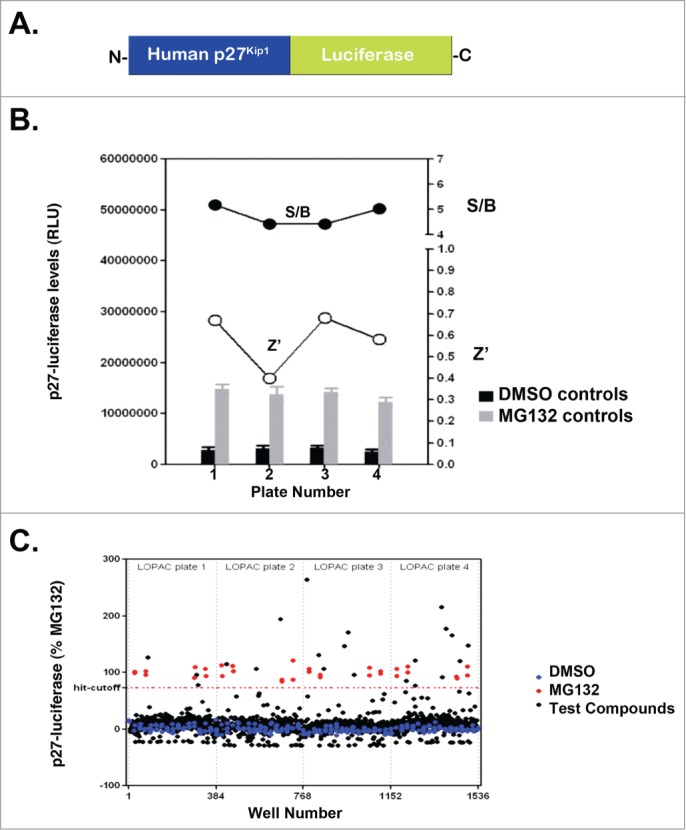
p27Kip1-luciferase is stabilized by compounds from the Library of Pharmacologically Active Compounds and MG132. (A) Diagram of p27Kip1-luciferase used in our studies. Note that luciferase is attached to the C-terminus of full-length human p27Kip1. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with p27Kip1-PGL4 plasmids and incubated with either MG132 or DMSO (vehicle control). After 24 hours, cells were lysed using BriteLite and the steady-state levels of luciferase measured. Results are from one representative experiment performed in quadruplicate. (C) p27Kip1-luciferase is stabilized by compounds in the Library of Pharmacologically Active Compounds (LOPAC). HeLa cells were transfected with the p27Kip1-luciferase plasmid and incubated with compounds from a library of pharmacologically active compounds (LOPAC). Cells were then lysed after 24 hours and the steady-state levels of luciferase measured. The hit-cutoff based on the average +3 SD calculation method was 73.16%. Based on this cutoff, 21 compounds were designated as hits, i.e., a hit rate of 1.64% (21/1280), which is in the expected range of 1–2% when screening a library of pharmacologically active compounds (otherwise a hit rate of <1% is expected). Further, there were no false positives among the DMSO wells and therefore the assay is not prone to false positives. The plate-to-plate variability of the raw luminescence values was kept below <15% (12% CV for DMSO control from one plate to another, 8% CV for the MG132 controls).
