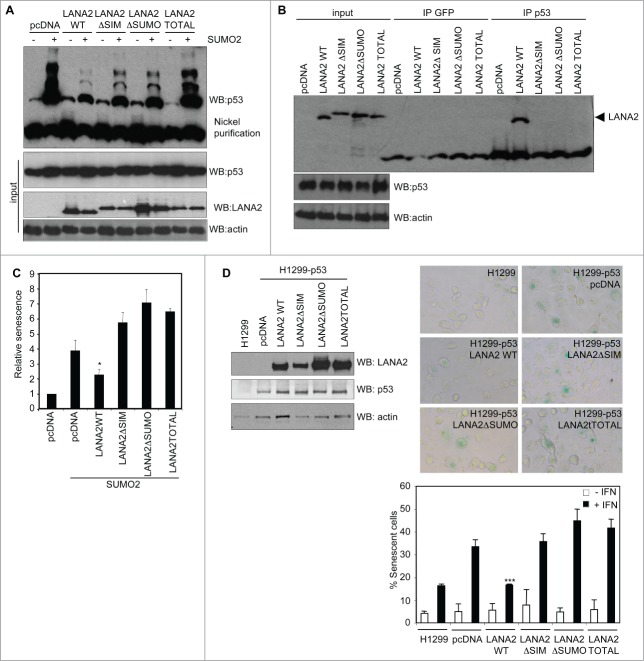
Figure 2.
LANA2 requires intact SIM and SUMOylation domains to inhibit p53-SUMO2 conjugation, to interact with p53, and to inhibit senescence induced by type I interferon treatment or SUMO2 overexpression. (A) LANA2 requires intact SIM and SUMOylation domains to efficiently reduce p53-SUMO2 conjugation. (B) Interaction between p53 and LANA2 requires intact SIM and SUMOylation domains in LANA2. (C) Inhibition of SUMO2-induced senescence by LANA2-WT but not by LANA2 mutants in the SIM or SUMOylation domains. Senescence was determined by using a senescence β-galactosidase staining kit. The results are presented as mean of 3 independent experiments +/− SD and analyzed by Student's t-test (*, P < 0.05 versus cells co-transfected with SUMO2 and pcDNA). (D) Inhibition of senescence induced by interferon treatment by LANA2-WT but not by the mutants of LANA2 in the SIM or SUMOylation domains. H1299-p53 cells transfected with LANA2-WT, LANA2ΔSIM, LANA2ΔSUMO or LANA2TOTAL were analyzed by Western blotting (upper-left panel) and treated or not with 500 U/ml β-interferon for 4 d after which cell senescence was evaluated by β-galactosidase staining. Representative pictures of SA-β-Gal staining (upper-right panel) and percentage of SA-β-Gal-positive cells (lower panel) in response to interferon treatment. The percentage of positive staining was determined by dividing the number of β-Gal-positive cells into the total number within 10 random fields. The results are presented as mean of 3 independent experiments +/− SD and analyzed by Student's t-test (***, P < 0.0005 vs. pcDNA transfected cells).