Figure 5.
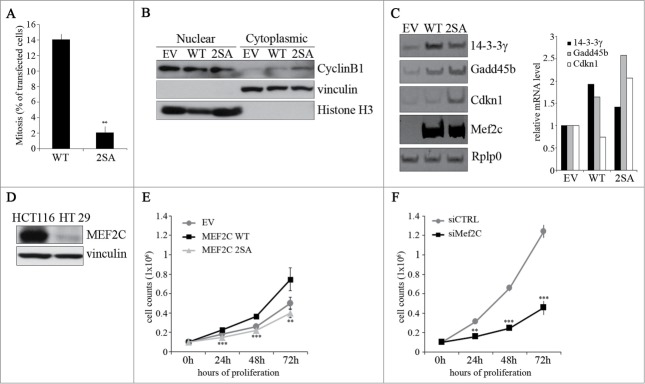
The ectopic expression of a stable, non phosphorylable mutant of MEF2C can delay cell cycle progression. (A) Overexpression of the MEF2C 2SA mutant is linked to a reduced number of mitotic events. COS-1 cells were transfected with vectors coding for wild type MEF2C (WT) or the not-phosphorylable FLAG-MEF2C 2SA mutant. 48 hours later cells were fixed for immunofluorescence analysis and stained with antibodies for phosphorylated histone H3 and FLAG. Transfected cells were scored for the frequency of mitosis. Histograms show means ± SEM of 2 independent experiments. ** represent P-values ≤ 0.01. (B) MEF2C 2SA impairs nuclear translocation of CYCLIN B1. HT29 cells transiently transfected with an empty vector (EV) or the expression vectors for the wild type or the not-phosphorylable MEF2C 2SA mutant were lysed in order to obtain nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extracts. The different fractions were analyzed by Western blotting with CYCLIN B1 antibody. Histone H3 and Vinculin antibodies were used as loading control respectively for nuclear and cytoplasmic fraction. (C) MEF2C regulates the expression of genes encoding inhibitors of the G2/(M) transition. Left panel, Total RNA was isolated from transfected C2 cells overespressing the wild type or 2SA MEF2C protein. The transcripts of Gadd45b, P21 and 14.3.3 γ genes were amplified by RT-PCR, PCR products were separated in 8% polyacrylamide gels. Rplp0 was used as endogenous control. The histograms in the right panel report the results of the densitometric quantification of the bands normalized to Rplp0 and expressed relatively to the empty vector transfected cells taken as 1. The RT-PCR results are representative of 2 independent experiments. (D) MEF2C is differentially expressed in CRC cell lines. Total protein extracts from HCT116 and HT29 proliferating cells were analyzed by Western blot with antibody against MEF2C. Vinculin was used as loading control. (E) MEF2C modulates cell cycle progression in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. HT29 cells were transfected with an empty vector (EV) or vectors coding for the wild type MEF2C protein or the non-phosphorylable MEF2C 2SA. After 24 hours, 0.1 × 106 cells were plated for each sample. Cells were then harvested every 24 hours and the number of proliferating cells were counted with an hemacytometer after Trypan blue staining. The graphs show means ± SEM of 4 independent experiments. Statistical significance of variation between values obtained at each time points with MEF2C 2SA and MEF2C WT was calculated. Differences between 2SA and WT are statistically significant. ** and *** represent P-values ≤ 0.01 and ≤ 0.001 respectively. (F) RNAi knockdown of Mef2c impairs HCT116 proliferation rate. HCT116 cells were transfected with a control siRNA (siCTRL) or a pool of siRNAs targeting Mef2c (siMef2c) and proliferation rate was evaluated as described in E. The graphs show means ± SEM of 4 independent experiments. ** and *** represent P-values ≤ 0.01 and ≤ 0.001 respectively.
