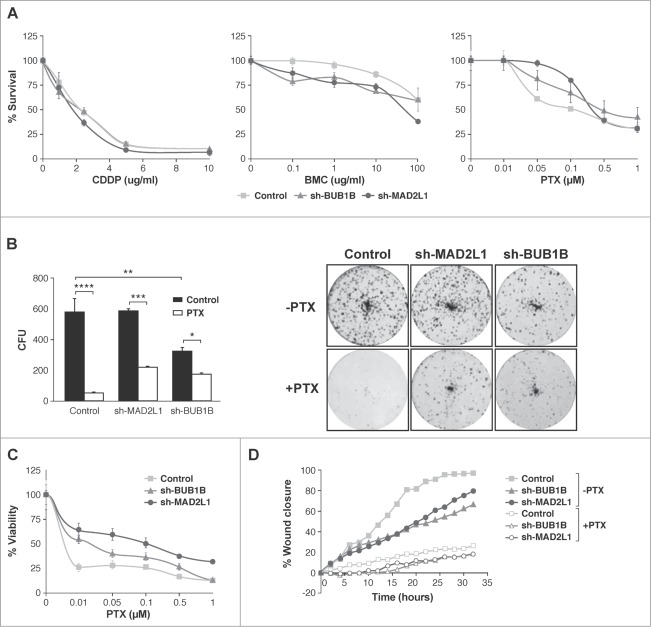
Figure 4.
Interference of Mad2 and BubR1 expression increases survival to PTX in MKN45 cells. (A) Indicated cell lines were seeded on MW96 and treated with increasing doses of CDDP, PTX or BMC. Graphs show survival curves measured by MTS 48 h after treatment. The experiments were performed in quadruplicate and repeated twice. (B) Left panel: Clonogenic assay. The graph represents the average of all clones in each experimental condition, in 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. Statistical significance was studied by a 2-way anova (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.005, *** P < 0.001). Cells were plated at low density and treated with 0.05 μM of PTX. Right panel: Representative images of colonies from a 10-day assay in control MKN45, sh-Mad2L1 and sh-BUB1B cell lines. (C) Control MKN45, sh-MAD2L1 and sh-BUB1B cells were treated with increasing concentrations of PTX (0–100 nM). Viability was quantified using the crystal violet after 48 h of treatment. Results are presented as percentage of viable cells relative to untreated cells. Data show the results from 3 independent experiments, performed in quadruplicate. Statistical differences were tested using Student's t-test (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.005, *** P < 0.001). (D) The effect of PTX (0.1 μM) on control MKN45, sh-Bub1B and sh-Mad2L1 cell migration in the wound healing assay was measured up to 48 h. The wound closure was quantified every 2 h postwounding by measuring the remaining unmigrated area using ImageJ.