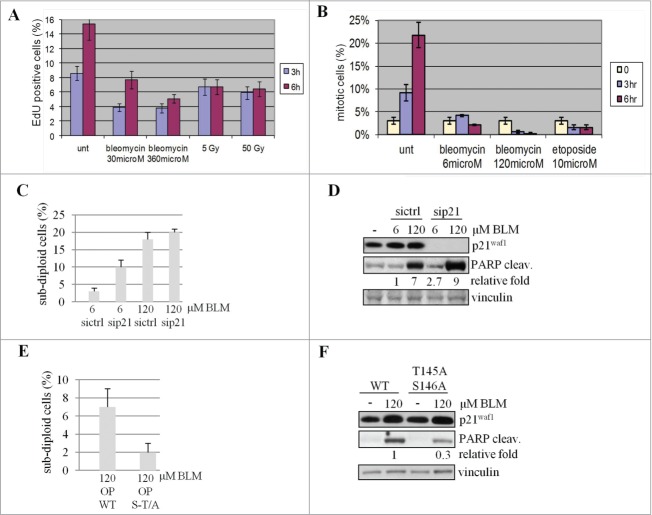
Figure 6.
p21Waf1 degradation impacts on apoptosis. (A) To assess G1 to S transition, LCL replicating cells were labeled with EdU and evaluated before and 3 and 6 hrs after the indicated DNA damaging treatments. The fraction of EdU positive cells before drugs addition or IR exposure was subtracted from each time point. (B) The G2 to M transition was assessed in U2OS cells pre-treated with 100 ng/ml nocodazole before exposure to genotoxic agents to trap cells in M phase to correctly enumerate cells entering in M phase avoiding mitosis exit. (C) U2OS cells were transfected with siRNA to knock down p21Waf1 (sip21) or a control sequence (sictrl). 48 hrs after transfection, cells were treated for 24 hrs with the genotoxic agents, stained with propidium iodide and the subdiploid apoptotic fraction quantitated by DNA flow cytofluorimetry. (D) The same cells were also lysed and tested for PARP cleavage by immunoblotting. The densitometric analysis of the cleaved form of PARP is shown after normalization on the 6 μM BLM sample. (E) U2OS cells transiently transfected with wild type (OP WT) or mutated (OP S-T/A) forms of p21Waf1, were exposed (72 hrs after transfection to reduce the amount of exogenous p21Waf1 protein and limit the impact of overexpression on cell cycle progression) for 24 hrs to BLM. The subdiploid apoptotic fraction quantified by DNA flow cytofluorimetry was evaluated as above. (F) The same cells were also lysed and tested for PARP cleavage by immunoblotting. The densitometric analyses of the cleaved form of PARP, normalized with vinculin and relative to the wt sample, are shown.