Figure 3.
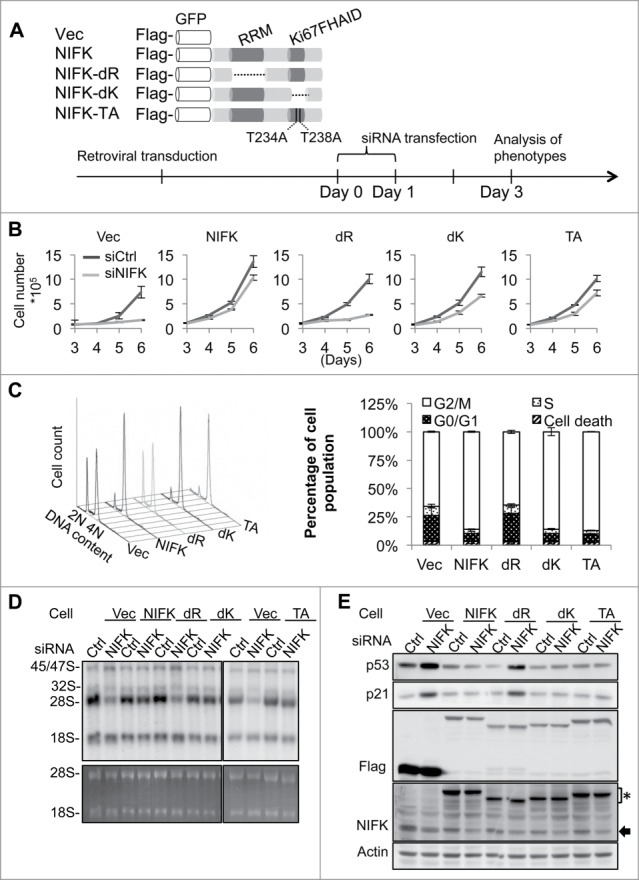
NIFK-mediated pre-rRNA processing and G1 progression require RRM but not Ki67FHAID. (A) Schematic representation of NIFK functional domains and designing of ectopic NIFK expression constructs (upper panel). For immuno and fluorescent detection, Flag-tag epitope and GFP were fused upstream of NIFK cDNA. dR indicates RRM deletion; dK, Ki67FHAID deletion; TA, T234AT238A; Vec, Flag-GFP vector. The procedure and time line for phenotypic rescue experiments are shown in the bottom panel. (B) Cell proliferation assay for cells phenotypically rescued by NIFK wild-type and mutants. (C) Flow cytometry analyses (left) and quantification (right) of rescued cells after G2/M synchronization. (D) 32P-orthophosphate based pulse-chase analysis showing the nascent rRNA synthesis in phenotypically rescued cells. 32P labeld RNAs at 4.5 h chasing time were visualized by autoradiography (upper panel) and EtBr staining (lower panel). (E) Western blot analysis showing p53 and p21 levels in the phenotypically rescued cells described in (D). Anti-NIFK antibody (NIFK) detects both endogenous and ectopically expressed NIFK. The asterisk indicates ectopic NIFK and the arrow, endogenous NIFK.
