Figure 3.
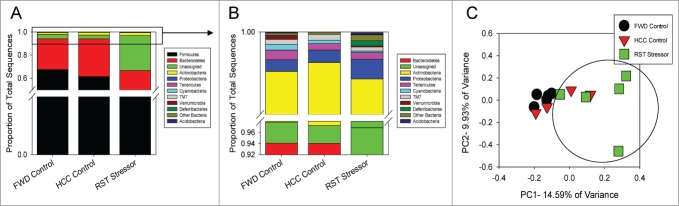
Stressor exposure significantly affects the community structure of the luminally-associated microbiota. (A) Major phyla were unchanged between any group. (B) Among the lesser phyla, Actinobacteria was significantly reduced in RST Stressor mice compared to both HCC Control and FWD Control, while Deferribacteres was significantly reduced in RST Stressor mice compared to HCC Control and FWD Control mice. Abundances were compared using non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis tests, and post-hoc testing was performed with non-parametric Mann-Whitney U tests. (C) Principle coordinate analysis was used to visualize stressor exposure-induced community profile clustering based upon unweighted Unifrac distances. RST Stressor shifted the community structure of the luminally-associated microbiota compared to FWD Control mice (P < 0.01) significantly using the ANOSIM statistic, but not significantly compared to HCC Control mice. FWD and HCC Controls were unchanged compared to each other. Data are from n = 5 for RST Stressor and FWD Control groups, and n = 4 for HCC Control.
