Figure 1.
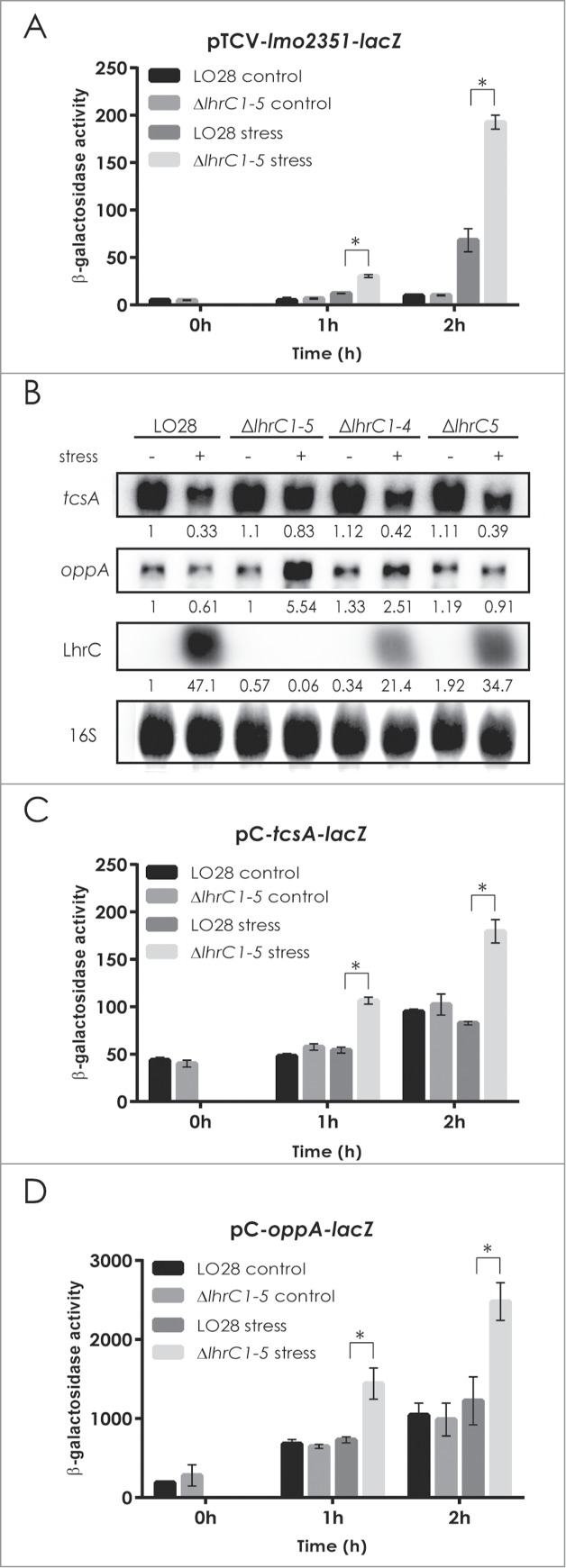
LhrC-mediated down-regulation of potential target genes. β-galactosidase activities were assessed in wild type and ΔlhrC1-5 strains carrying a transcriptional reporter gene fusion of the lmo2351 promoter to lacZ in pTCV-lac (A), or translational reporter gene fusions of tcsA (C) and oppA (D) to lacZ in the vector pCK. β-galactosidase activity of wild type and mutant cells was measured at the indicated time-points under non-stress conditions (control samples) and after exposure to 4 µg/ml cefuroxime (stress). Results of the β-galactosidase assays are the average of 3 biological replicates each conducted in technical duplicates. After 1 and 2 hours of stress, a significant difference between the mutant and wild type cells was observed for all 3 reporter gene fusions tested (asterisk: P < 0.005). (B) Northern blot analyses of tcsA mRNA, oppA mRNA and LhrC. Samples were taken from LO28 wild type, ΔlhrC1-5, ΔlhrC1-4 and ΔlhrC5 cultures exposed to 1 hour of cefuroxime stress (+) as well as from non-stressed cultures (−). Northern blots were probed for tcsA mRNA, oppA mRNA, LhrC and 16S (loading control). Relative levels of tcsA mRNA, oppA mRNA and LhrC (normalized to 16S) are shown below each lane.
