Figure 5.
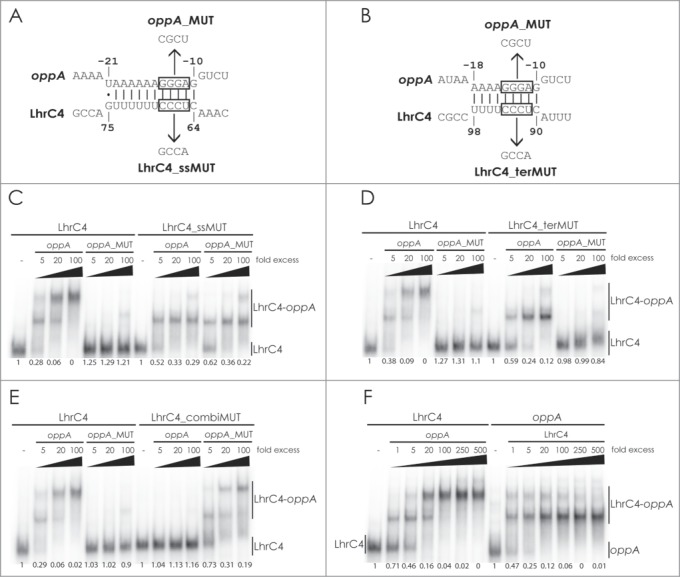
Gel mobility shift assay of the interaction between LhrC and oppA mRNA. Deduced binding of the CU-rich region of the single-stranded stretch (A) or terminator loop (B) of LhrC4 to oppA mRNA. The UCCC motifs in LhrC4 and the complementary GGGA sequence in oppA mRNA are boxed. Sequences of the minimal mutant variants oppA_MUT, LhrC4_ssMUT and LhrC4_terMUT are shown. The double mutant LhrC4_combiMUT contains the substitutions of both LhrC4_ssMUT and LhrC4_terMUT. For gel mobility shift assays, labeled wild type LhrC4 and labeled mutant variants LhrC4_ssMUT (C), LhrC4_terMUT (D) or LhrC4_combiMUT (E) were incubated with increasing concentrations of unlabeled wild type oppA RNA or the mutant variant oppA_MUT. (F) Equal amounts (40 pmol) of labeled LhrC4 (left) or labeled oppA RNA (right) were incubated with increasing concentrations of unlabeled oppA RNA or LhrC4, respectively. The fraction of unbound LhrC4 or oppA RNA is shown below each lane.
