Figure 1.
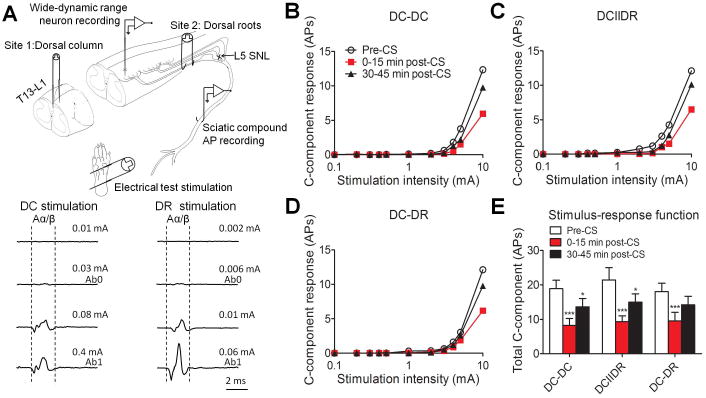
Effects of different patterns of conditioning stimulation (CS) at moderate intensity on WDR neuronal response to graded electrical stimuli. (A) Upper: A schematic diagram shows the experimental paradigm used in the neurophysiologic studies. Antidromic sciatic compound action potential (AP) was evoked by graded electrical stimulation (0.001-5.0 mA, 0.2 ms, biphasic) applied at the dorsal column (DC) and dorsal root (DR). Lower: The intensities that produced the first detectable Aα/β waveform (Ab0) and the peak Aα/β waveform (Ab1) were determined. (B-D) The stimulus–response functions of C-component of WDR neuronal response to graded intra-cutaneous electrical stimulation (0.1-10 mA, 2 ms) before and after different patterns of CS (DC-DC: n = 21; DCIIDR: n = 21; DC-DR: n = 20 neurons) at the moderate stimulus intensity of 50%(Ab0+Ab1) in SNL rats. For clarity, error bars are not shown. (E) The total number of action potentials in the C-component before and after CS. Data are expressed as mean + SEM. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 as compared with the pre-CS baseline.
