Figure 5.
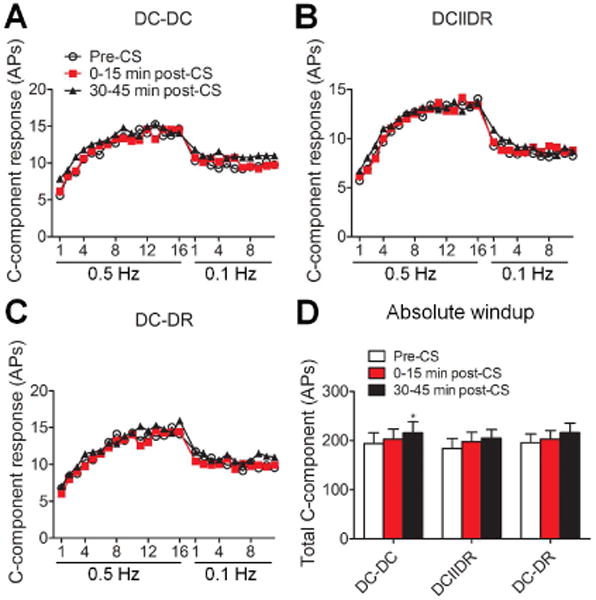
Effects of different patterns of low-intensity conditioning stimulation (CS) on windup. (A-C) C-component of WDR neuronal responses to a train of electrical stimuli at a frequency of 0.5 Hz (16 pulses, 2.0 msec, 1.5 × C-th) and then at 0.1 Hz (12 pulses, applied 30 seconds after the cessation of 0.5-Hz stimulation) were plotted against the stimulation sequence number (DC-DC: n = 17; DCIIDR: n = 17; DC-DR: n = 16 neurons). For clarity, error bars are not shown. (D) The area under the windup function to a 0.5 Hz train pre-CS, 0-15 minutes post-CS, and 30-45 minutes post-CS at the low intensity of Ab0 was compared in each group. Data are expressed as mean + SEM. *P<0.05 as compared with the pre-CS baseline. AP: action potential, DC: dorsal column, DR: dorsal root.
