Figure 1.
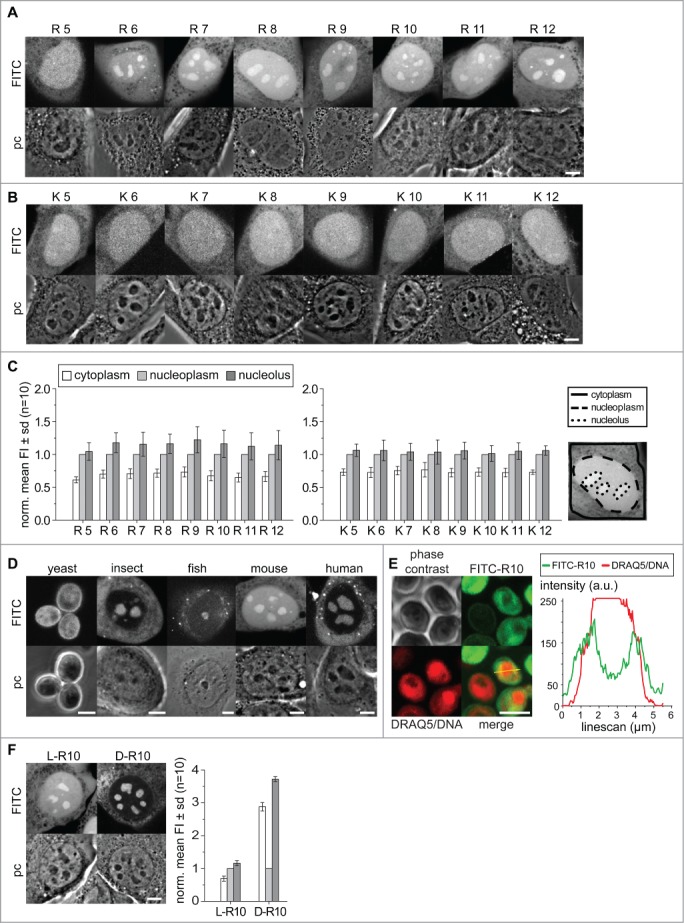
Distribution of poly-(R)and poly-(K)peptides in living cells. Intracellular distribution of poly-R peptides in (A) and poly-K peptides (B) in living C2C12 mouse cells. In each panel, the fluorescence image is on top of the corresponding phase contrast image. Nucleoli are clearly visible as dark round structures within the nuclei in the phase contrast images. The bar diagrams in (C) show the quantification of the poly-K and poly-R peptide mean fluorescence in cytoplasm, nucleoplasm and nucleoli averaged for 10 cells from 2 independent experiments. The nucleoplasmic values were used for normalization. Areas for quantification were defined as described in methods and overlayed with fluorescence images as shown. Intracellular distribution of R10 peptide in living cells of different species as indicated is shown in (D). In (E) living yeast cells were further stained with DRAQ5 for better visualization of the nucleus and a line intensity profile in arbitrary units (a.u.) of both DNA and peptide is shown. The intracellular distribution of (D) and L-R10 peptides in living C2C12 cells and the corresponding quantification of mean fluorescence intensities is shown in (F). Scalebars: 5 µm.
