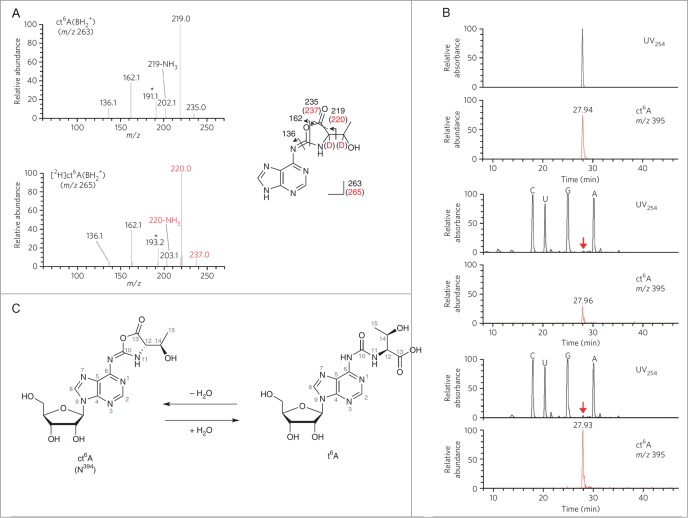
Figure 2.
Structural determination of N394. (A) The CID spectra of unlabeled (top) and deuterium (D)-labeled (bottom) ct6A bases (BH2+). The product ions are assigned in the chemical structures of the ct6A base. D-labeled product ions are shown in red. Unassigned spectra containing the D-labeled portion are indicated by asterisks. (B) LC/MS coinjection of the synthetic and natural ct6A. UV traces (254 nm) and mass chromatograms (m/z 395) of synthetic ct6A (top), natural ct6A in E. coli total RNA (middle) and co-injected natural and synthetic ct6A (bottom). ct6A peaks in the UV trace are indicated by red arrows. (C) The chemical structures of ct6A and t6A are mutually convertible by hydration and dehydration. Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature Chemical Biology, volume 9, pages 105–111 (2013).