Figure 3.
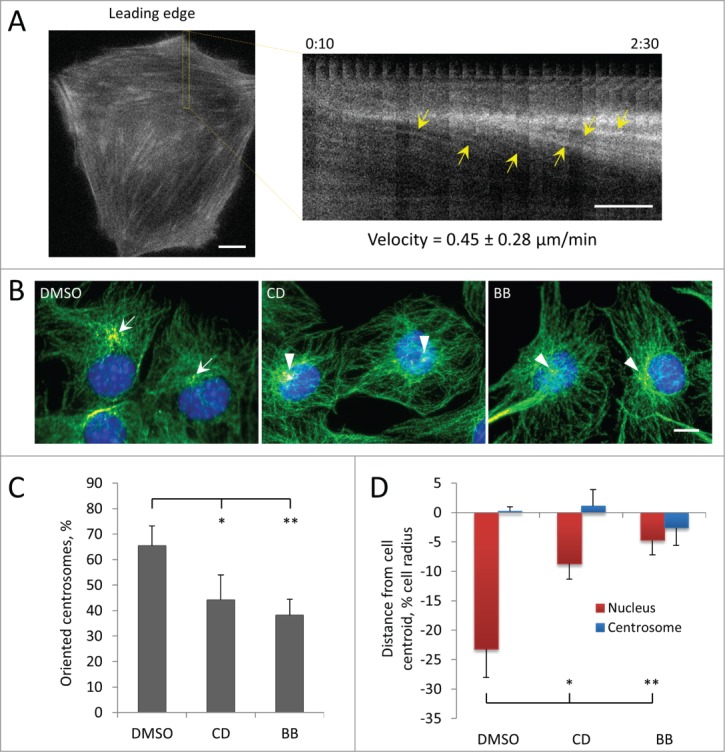
Centrosome orientation and nuclear movement in wounded monolayers of serum-starved C2C12 myoblasts depends on actin and myosin II. A, Initial panel (left) and kymograph (right) from the indicated region showing the rearward movement of actin cables (yellow arrows) in the lamella from a fluorescence movie of a LPA-stimulated, wound-edge C2C12 myoblast expressing LifeAct-mCherry. Time is in hr:min after LPA treatment. The velocity of actin cable movement from 12 cells is indicated. B, Immunofluorescence images of microtubules (green), pericentrin (red) and nuclei (blue) in LPA-stimulated C2C12 myoblasts at the edge of a wounded monolayer after treatment with vehicle (DMSO), 0.5 μM cytochalasin D (CD) or 25 μM blebbistatin (BB). Arrows indicate oriented centrosomes; arrowheads indicated unoriented centrosomes. C, Quantification of centrosome orientation in LPA-stimulated C2C12 myoblasts treated with actin and myosin II inhibitors as in B. D, Positions of the nucleus and the centrosome in LPA-stimulated C2C12 myoblasts treated with actin and myosin II inhibitors as in B. Bars in A and B, 10 μm. Error bars in C and D are SD from 3 experiments (n > 30 cells per experiment). *, P < 0 .05; **, P < 0 .01 by t-test.
