Figure 3.
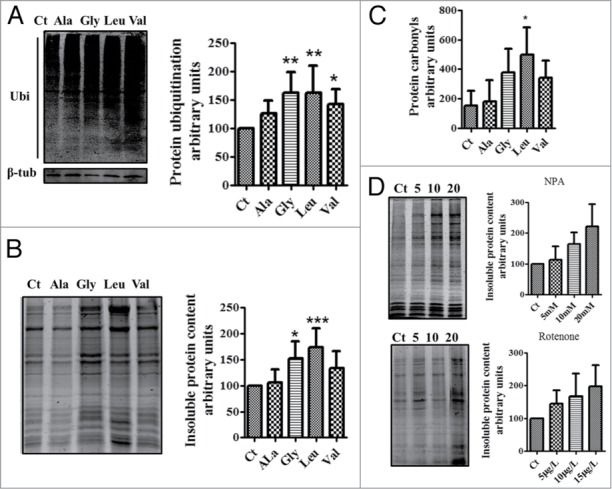
Mistranslation increases the levels of protein ubiquitination and aggregation. (A) western blot analysis showing that mistranslated proteins are poliubiquitinated. Data showed are the mean ± SD (n = 6). (Data analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by a Dunnet test with CI 95% relative to Ct; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05). (B) Mutant proteins produced by Ser misincorporation accumulate in insoluble aggregates, especially in embryos expressing the Ser-tRNAUCCGly, Ser-tRNACACVal and Ser-tRNACAGLeu. Representative gel showing the insoluble protein fraction of control and mistanslating zebrafish embryos. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 5). (Data analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by a Dunnet test with CI 95% relative to Ct; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05). (C) Gels showing that mistranslation increases the levels of protein carbonylation. Errors bars represent the standard deviation of four independent experiments (Student's unpaired t test, *P ˂ 0.05). (D) Gels showing that oxidative stress generates protein aggregation in zebrafish. Embryos incubated with the mitochondrial electron transport chain disruptors 3-Nitropropionic acid (NPA) and Rotenone had high levels of insoluble proteins. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). Units are relative to control sample in percentage. Western blot and SDS-page samples were normalized for the gel control sample.
