Figure 6.
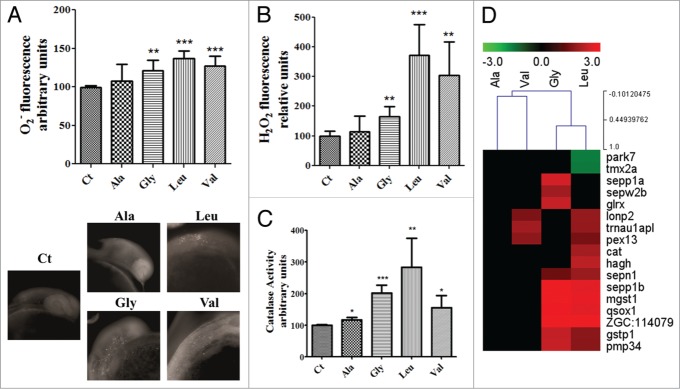
Oxidative stress is one of the endpoints of mistranslation. (A) The detection of the superoxide anion with dihydroethidium by fluorimetry (a) and microscopy (b) showed a discrete increase in its levels in the mutant embryos expressing the mutant tRNAs. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 5) (Student's unpaired t test, **P ˂ 0.005, ***P ˂ 0.0001 was used for data statistical analysis). (B) Hydrogen peroxide levels were highly increased in the mistranslating embryos. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 4) (Student's unpaired t test, **P ˂ 0.01, ***P ˂ 0.001). (C) Catalase activity was also induced by mistranslation, balancing the increase in the production of hydrogen peroxide. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 4) (Student's unpaired t test, *P ˂ 0.05, **P ˂ 0.01, ***P ˂ 0.0005). (D) Cluster representation of redox maintenance and antioxidant defense genes deregulated in mistranslating embryos, showing that these genes are mainly upregulated, with the strongest upregulation in embryos expressing the Ser-tRNAUCCGly and the Ser-tRNACAGLeu. Units are relative to control sample in percentage.
