Figure 2.
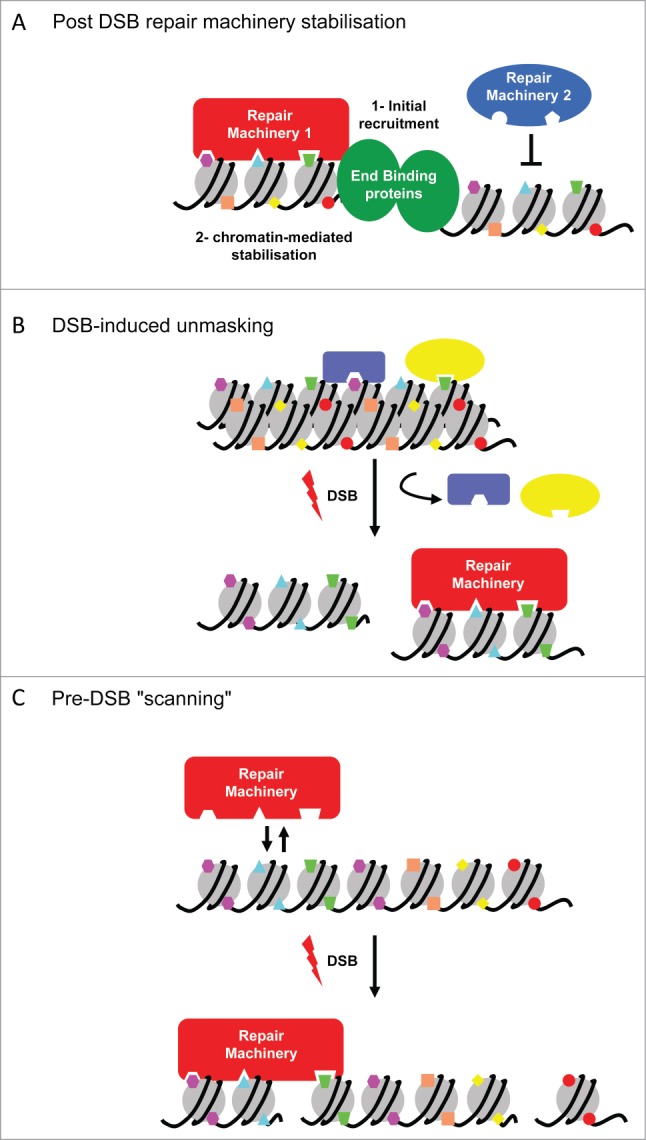
Potential mechanisms for preexistent chromatin structure in addressing repair pathways. (A) Following DSB and initial recognition by end binding proteins, such as Ku or the MRN complex, chromatin modifications already present at the break will stabilize component of a specific DNA repair pathway and/or inhibit association of component from another pathway. (B) DSB induces unmasking of existing histone marks by chromatin structure remodeling and/or chromatin reader eviction, making these modifications available for recognition by DNA repair factors. (C) In undamaged chromatin, repair proteins may preferentially interact with certain region of the genome based on their specific chromatin signature, facilitating their loading upon DSB induction.
