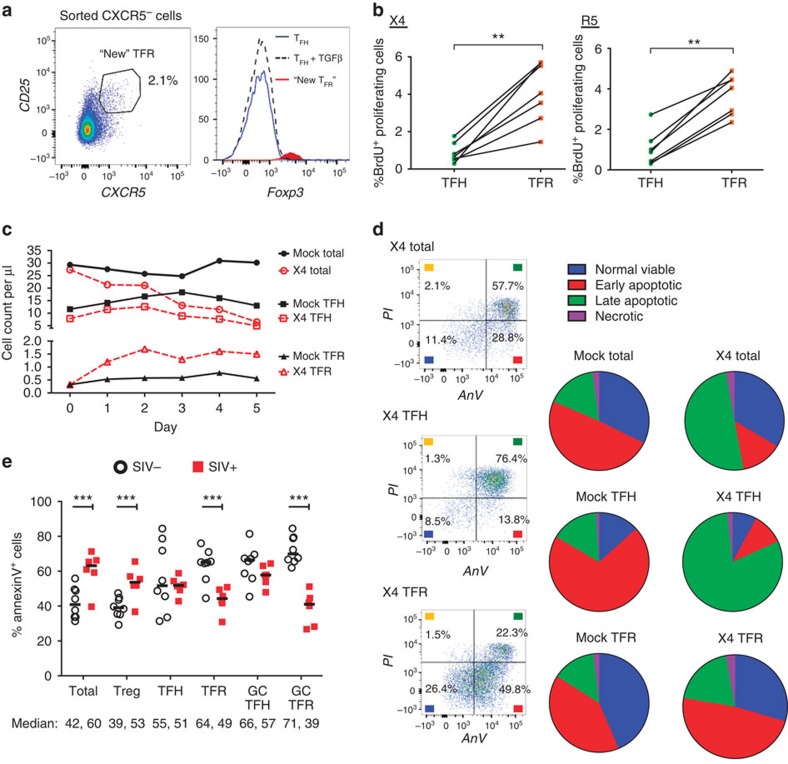
Figure 5. Acquisition of CXCR5, enhanced proliferation and reduced apoptosis promote TFR expansion.
(a) TFH and CXCR5− T-cell populations were sorted and cultured without stimulation, or TFH were cultured in the presence of exogenous TGF-β (100 ng ml−1). CXCR5 expression was analysed on sorted CXCR5− cells after 2 days and cells expressing CXCR5 are labelled as ‘new TFR'. The Foxp3 expression levels of TFH, TFH cultured with TGF-β and ‘new' TFR were determined (n=3). (b) TFH and TFR were mock-, X4- or R5-spinoculated and cell proliferation measured by BrdU incorporation after 2 days of culture (n=7). (c,d) A 5-day time course was performed to monitor T-cell population counts and rates of cell death with mock- or X4-spinoculated tonsil cells (n=3). (c) Average counts of total (CD3+CD8−, circles), TFH (CXCR5+CD25lo/−, squares) and TFR (CXCR5+CD25hiCD127−, triangles) are shown for the duration of culture (n=3). (d) Stages of cell death are shown at day 5 and defined as early apoptosis (AnnexinV+), late or advanced apoptosis (AnnexinV+ PI+) and necrotic death (PI+; n=3). (e) Cell subsets from disaggregated lymphoid tissues of chronically SIV-infected (n=6) and uninfected rhesus macaques (n=8) were analysed for apoptosis by percent Annexin-V binding. Cell phenotypes were defined as total (CD3+CD8−), Treg (CD3+CD8-CD25hiCD127−), TFH (CD3+CD8-CXCR5+CD25lo/−), TFR (CD3+CD8-CXCR5+CD25hiCD127−), GC TFH (CD3+CD8-CXCR5+PD1hiCD25lo/−) and GC TFR (CD3+CD8-CXCR5+PD1hiCD25hiCD127−). Statistical analyses were performed by Wilcoxon matched-pairs tests (b) or Mann–Whitney tests (e) and significance is denoted by asterisks where **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.