Figure 4.
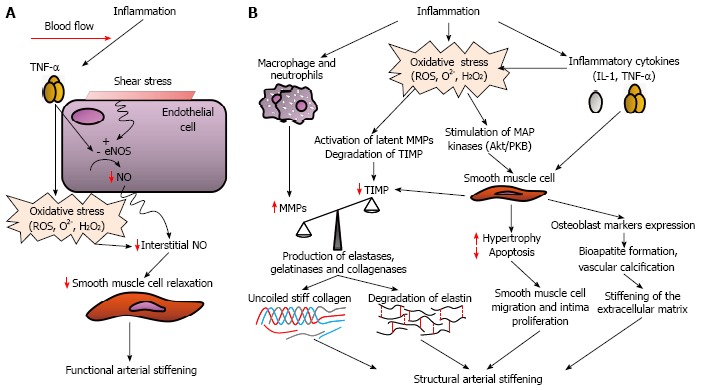
Potential mechanisms by which inflammation can induce functional (A) and structural (B) arterial stiffening. eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; IL-1: Interleukin-1; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; NO: Nitric oxide; O2-: Superoxide; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
