Figure 7.
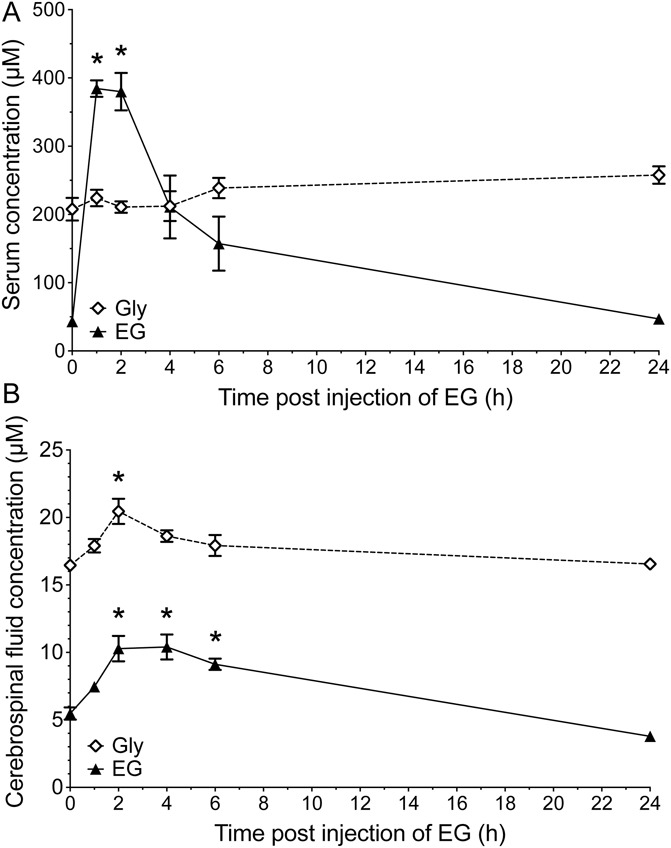
Subcutaneous injection of N-ethylglycine (EG) in rats leads to an increased EG concentration in blood serum and to increased EG and glycine (Gly) concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid. Concentrations of EG and glycine were determined using high-pressure liquid chromatography in (A) blood serum and (B) cerebrospinal fluid samples from adult rats before and at indicated time points after subcutaneous injection of EG (200 mg/kg). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 4 per group; *P < 0.05 vs before injection of EG; 1-way analysis of variance and Bonferroni post hoc test.
