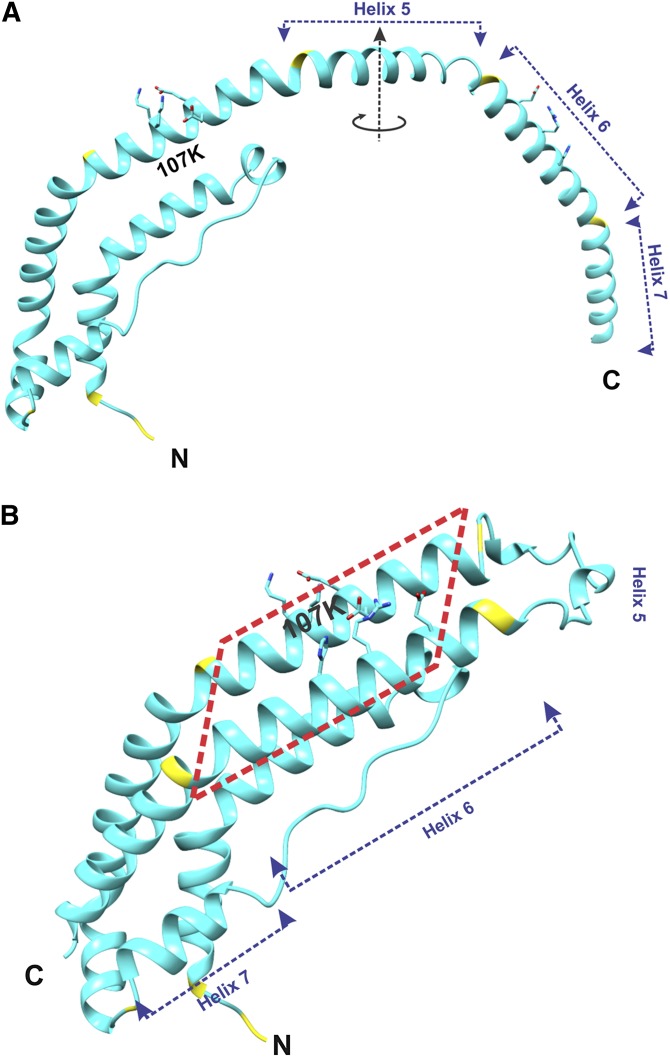
Fig. 2.
Structure of the lipid-free C-terminally truncated apoA-I monomer. Location of K107 is shown. A: Overall structure of one molecule of apoA-I[Δ(185-243)] from the crystallographic dimer shown in Fig. 1A. The circular arrow around the dimer 2-fold axis (in the middle of Helix 5) shows the direction of folding back the helical repeats 6 and 7 upon the conversion of the apoA-I dimer conformation to the monomer conformation [shown in (B)]. B: Structure presumed for the C-terminally truncated apoA-I monomer in solution. This monomer structure of apoA-I[Δ(185-243)] was obtained from the structure of one molecule in the crystallographic dimer [shown in (A)] that is folded back in the middle of the central helix 5. The two conformational states [(A) and (B)] are proposed to interconvert dependent on protein concentration [(A) at high concentrations, when dimers are formed, and (B) at low concentrations, when protein is monomeric]. The red dashed rectangle outlines a part of the proposed monomer structure that corresponds to the part of the crystallographic dimer outlined similarly in Fig. 1.