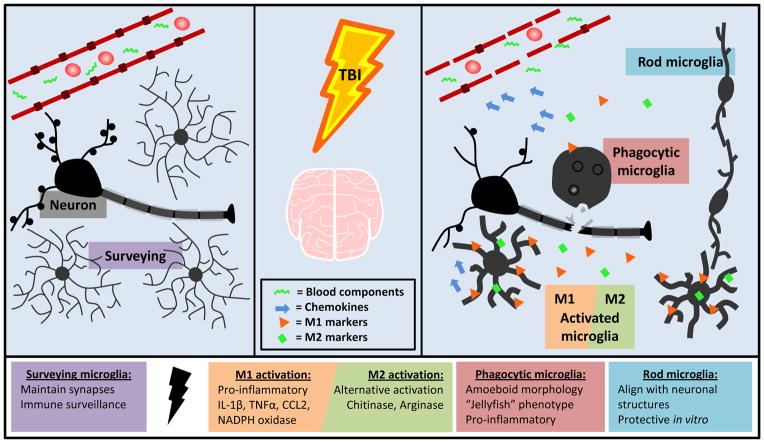
FIGURE 2. Microglia are acutely activated following TBI and take on a variety of functional and morphological states.
Microglia in their “resting” state are constantly surveying the environment and maintaining homeostasis. Following TBI, microglia are activated by cell debris, neuronal injury, and blood components. Microglia produce the chemokine CCL2, which plays a role in attracting peripheral monocytes to the CNS. Microglia upregulate both M1 and M2 cytokines and surface markers after injury. M1 activation results in production of ROS and RNS and up regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and surface markers including IL-1β, TNFα, and CD14. These activated cells can become phagocytic to clear debris. M2 activation is neuroprotective and indicated by upregulation of chitinase and arginase. Rod microglia align with neuronal structures after diffuse injury and are neuroprotective in vitro.