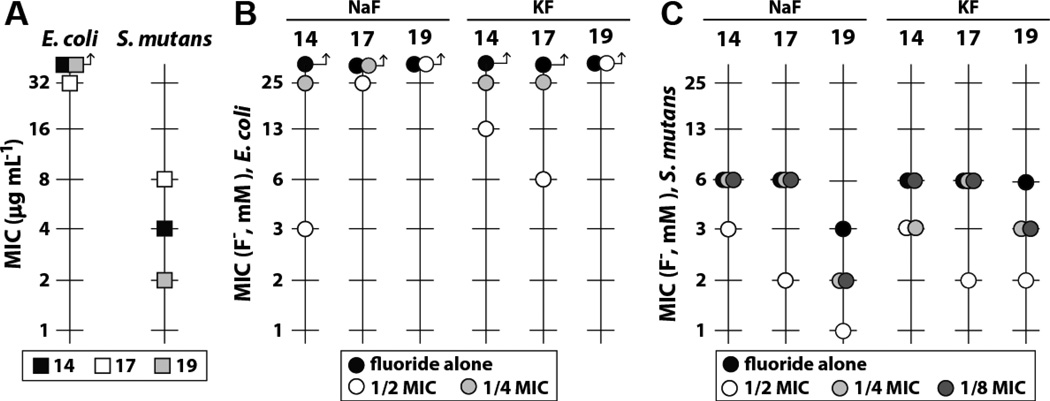
Figure 5. Structural derivatives of hit compounds enhance fluoride toxicity.
(A) MIC of hit compounds for E. coli and S. mutans in the absence of fluoride. Arrows indicate that the values for the analyses denoted by the symbols were not measurable at the highest concentrations tested.
(B) Decrease in the MIC of sodium or potassium fluoride for E. coli in the presence of varying concentrations of hit compounds. For compounds whose MIC in the absence of fluoride was higher than 32 µg ml−1, half and quarter MIC values were calculated as if the MIC were 64 µg ml−1. Values are the average of three replicates.
(C) Decrease in the MIC of sodium or potassium fluoride for S. mutans in the presence of varying concentrations of hit compounds. Values are the average of three replicates.