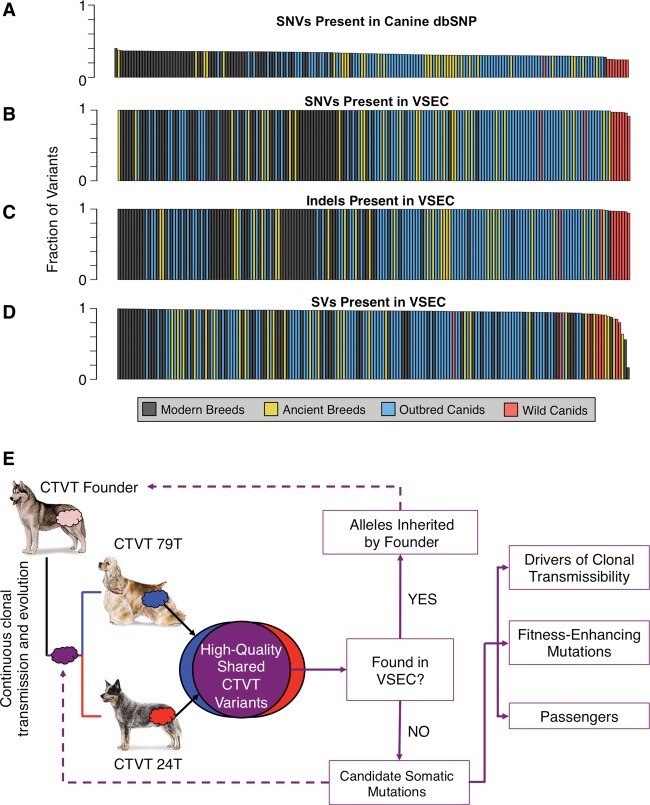
Figure 1.
Founder-inherited versus somatic variation in CTVT. (A) Fraction of SNVs from 186 sequenced canids found in canine dbSNP (mean 32.65%). Sequenced canids included the two host dogs, 64 dogs representing 40 modern breeds, 27 dogs representing 12 ancient breeds, 86 outbred canids spanning four continents, and nine wild canids. (B–D) Fraction of SNVs, indels, and SVs found in a single canid that are present in at least one other canid in the panel (means of 99.55%, 99.57%, and 95.63%, respectively). (E) High-quality variants found in both CTVT tumors were compared against our Variant and Systematic Error Catalog (VSEC), which was generated from 186 canid whole-genome sequences. Consensus CTVT variants present in the VSEC catalog were presumed to be alleles inherited by the founder canid. Novel variants were treated as somatic mutations, some of which are crucial to clonal transmissibility. Dog images are from the American Kennel Club (http://www.akc.org).