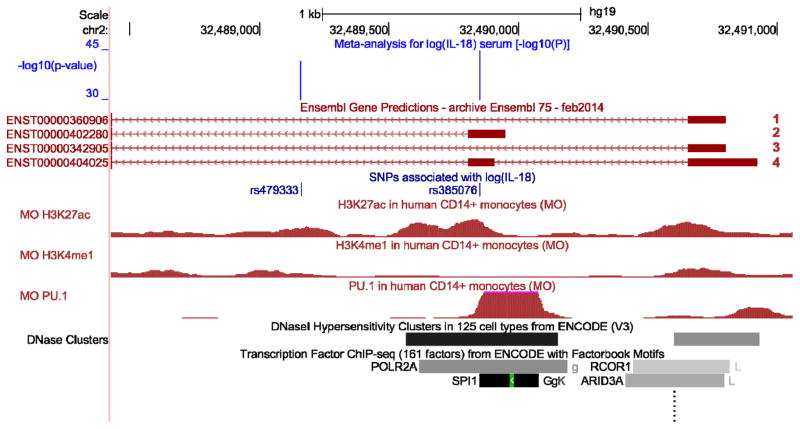
Figure 3.
In silico functional analyses for rs385076 within the NLRC4 gene region. Co-localization of IL-18 associated variants and regulatory and epigenetic features were investigated in the UCSC Genome Browser (genome-euro.ucsc.edu) using genome release hg19. Only SNPs with P-values <5×10−8 for the association with circulating IL-18 levels are shown (green track). Tracks showing histone modifications and PU.1 binding sites were uploaded into the UCSC Genome Browser from an external study22 (red tracks). The PU.1 track represents binding sites of the transcription factor PU.1 in monocytes from a CHIP-seq experiment. The H3K27ac track shows histone modification by acetylation from CHIP-seq experiments in monocytes, which can be considered as a mark for active enhancers26. The H3K4me1 mark shows regions undergoing histone methylation, which are likely to reflect cell-type specific regulation of a gene27. Enhancer regions are highlighted by DNaseI hypersensitivity clusters from the ENCODE project21. In the bottom track, CHIP-seq results for transcription factors (TF) from the ENCODE project are shown, indicating TF binding regions. rs385076 falls into the 5‘UTR exon of NLRC4 and a binding region of PU.1. DNase hypersensitivity clusters around rs385076 suggest a good DNA accessibility in monocytes and histone modification data highlights the region as an enhancer.