Figure 2. Integration of immune signaling pathways with PD regulation.
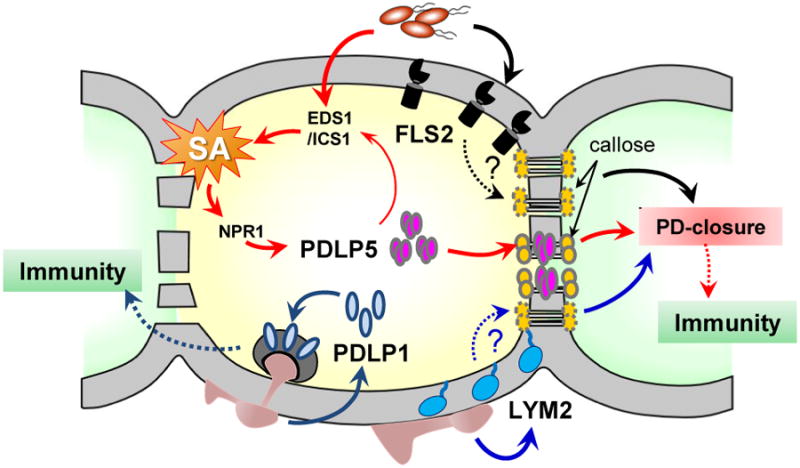
Recognition of different PAMPs by FLS2 or LYM2 leads to a PD closure. Whether these two receptors require callose-mediated mechanism in closing PD is not known. Elevated SA concentration in response to microbial infection induces the expression of PDLP5, whose feedback amplifies SA accumulation by unknown mechanism. PDLP5 partitions to PD and activates PD-callose deposition, which results in a PD closure. PDLP1 facilitates immune responses during fungal infection through relocation to the haustorial membrane surrounding infection sites.
