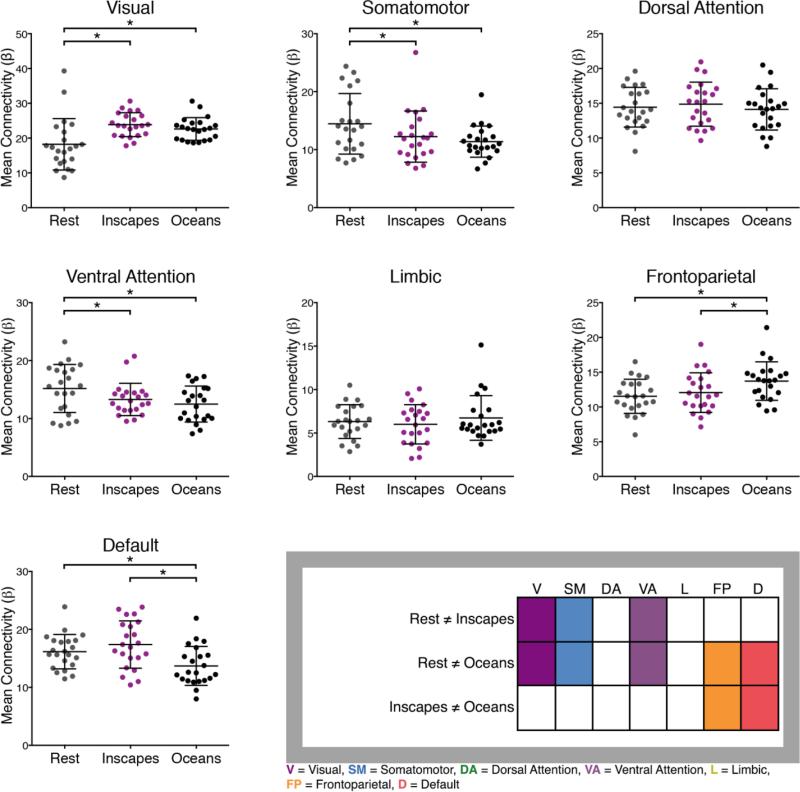
Figure 8. Mean network functional connectivity (FC) in healthy adults across different acquisition conditions, n = 22.
A dual regression analysis was used to obtain mean voxel-wise FC scores for each network for each subject (Filippini et al., 2009). Network masks were based on the Yeo 7-network scheme (Yeo et al., 2011). To evaluate differences in mean FC, we performed a series of repeated-measures ANOVAs to test for effect of condition (Inscapes, Oceans, Rest). A significant main effect of condition on mean FC was demonstrated for 5 out of 7 networks, with no significant difference observed for the dorsal attention and limbic networks. The table in the bottom right summarizes the results of the post hoc t-tests, with colored boxes indicating those networks that exhibited significant differences across conditions. The visual, somatomotor and ventral attention networks differed significantly for both movies when compared to Rest, while no significant difference was found across the movies. Additionally, the frontoparietal and default networks differed significantly between Oceans and Rest and Oceans and Inscapes, while no significant difference was found across Inscapes and Rest.