Figs 51–58.
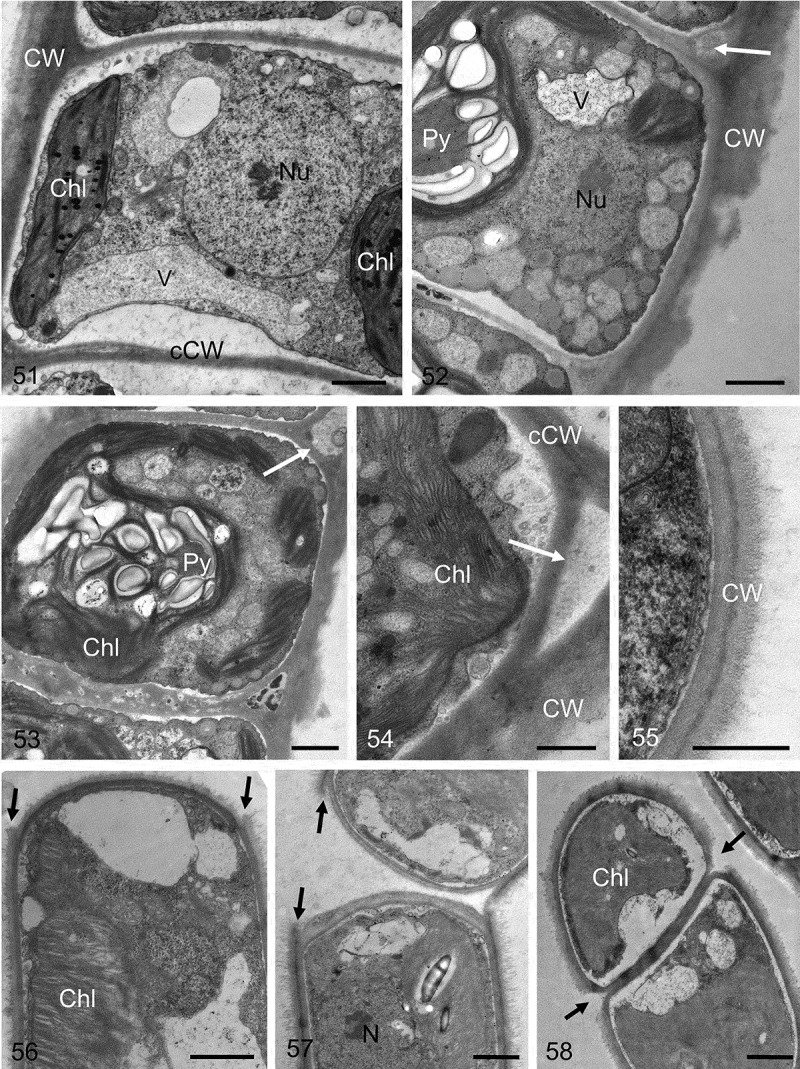
Transmission electron micrographs of different Klebsormidium strains. Fig. 51. Central nucleus and parietal chloroplast clearly visible. Fig. 52. Chloroplast contains pyrenoid, the outer cell wall exhibits clear layering with a corrugated outer surface, and the triangular space between the outer cell wall and the cross-wall is marked with a white arrow. Fig. 53. Pyrenoid with numerous starch grains, triangular space is marked with a white arrow. Fig. 54. Triangular space (white arrow) between the outer cell wall and the cross-wall. Fig. 55. Double-layered outer cell wall. Fig. 56. Terminal cell, showing the projections of the mother-cell wall (black arrows). Fig. 57. Two cells still not fully separated, showing the projections of the mother-cell wall (black arrows). Fig. 58. Initiating separation of two cells, the mother-cell wall is already separated (black arrows). Material illustrated is: Figs 51–54, Klebsormidium crenulatum (SAG 2415); Fig. 55, Klebsormidium dissectum (SAG 2416); Figs 56, 57, Klebsormidium nitens (SAG 2417); Fig. 58, Klebsormidium cf. nitens (STR1). Abbreviations: Chl, chloroplast; CW, cell wall; cCW, cell cross-wall; Nu, nucleus; Py, pyrenoid; V, vacuole. Scale bars Figs 51–53, 56–58, Figs 54–55: 1 µm; d, e: 500 nm.
