Fig. 68.
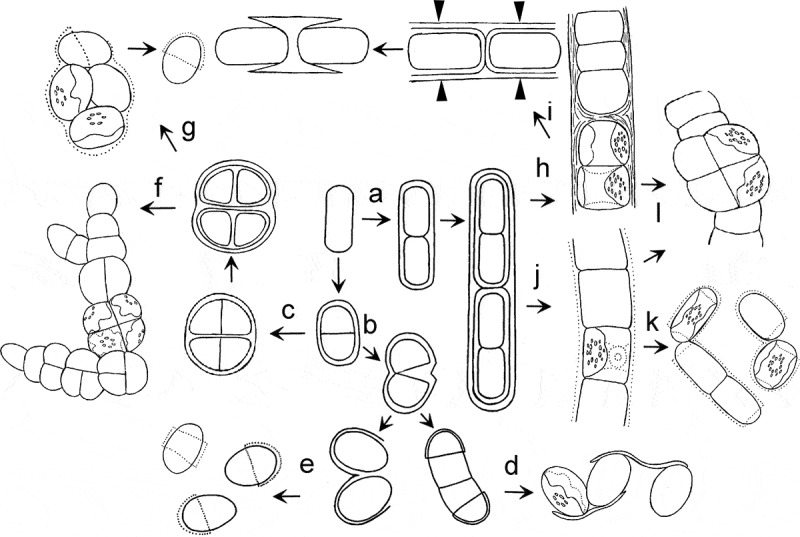
Scheme showing different routes of transformation of the Interfilum and Klebsormidium parental-cell wall, leading to formation of different morphotypes. a: preservation of parental wall, cylindrical cells divided mostly in one plane; b: gelatinization or rupture of parental wall; c: preservation of parental wall, almost-spherical cells divided in several planes; d: formation of unicells connected by ‘threads’; e: formation of unicells with cap- and ring-like structures; f: formation of packets and branched thallus; g: gelatinization of parental wall and formation of unicells with cap-like structures; h: preservation of parental wall, formation of strong filaments; i: formation of H-like fragments; j: partial gelatinization of parental wall; k: formation of short filaments, dyads and unicells; l: occasional division in several planes, formation of packet-like structures and biseriate parts. Arrowheads indicate sites of rupture of parental wall.
