Fig 2. Distribution of molecular and cellular properties of orthologous DHFRs.
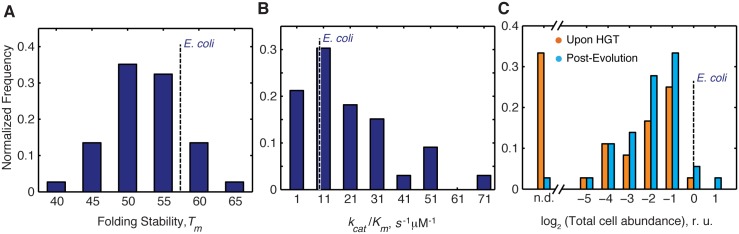
A) Distribution of Tm values of the purified DHFR proteins assessed by thermal unfolding in a Differential Scanning Calorimeter (see Materials and Methods). The proteins span wide range of stability between 42–63°C, as expected for mesophilic proteins, with ~80% of proteins having higher stability than E.coli DHFR. (see also S1 Table). B) Distribution of catalytic activity (k cat/KM) of the purified DHFRs (see Materials and Methods, and S1 Table). ~70% purified DHFR proteins were found to have activities that are comparable to or better than E. coli DHFR. C) Intracellular abundance (measured in total cell lysate) of DHFR before and after evolution experiment assessed by Western Blot with polyclonal anti-His antibodies (see Materials and Methods). Abundance is expressed relative to that of E. coli DHFR. Strains for which abundances were too low to be detected are denoted as n.d. After the evolution experiment, a large number of strains have detectable abundance (~97% compared to ~70% before evolution) (S1 Table and S5 Fig) Overall, there is a significant shift in the abundance distribution for all proteins after evolution experiment (KS p-value = 0.049).
