Fig 5. Sequencing of the orthologous strains.
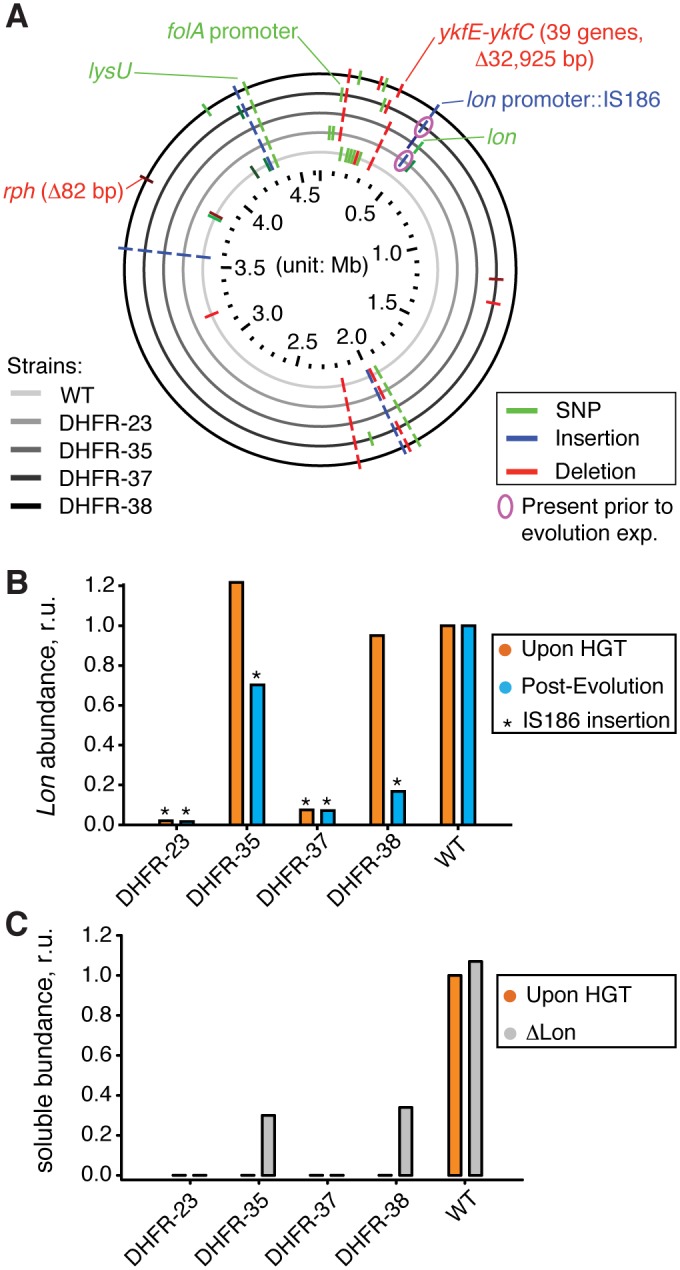
A) Mutations detected by whole genome sequencing (WGS) in the evolved populations of WT and orthologous DHFR-23, 35, 37, and 38 strains are indicated with respect to their location in E. coli chromosome. Only mutations that exceed 20% frequency in a population are shown (see S4 Table for detailed sequencing results). Mutations validated by PCR followed by Sanger sequencing (S5 Table), or known from literature are annotated. IS186 insertion in clpX-lon intergenic area was also found in naive DHFR-23 and 27 strains (i.e., prior to evolutionary experiment) (pink circle). B) Intracellular Lon abundance decreases upon intergenic clpX-lon IS186 insertion. Intracellular Lon abundance in total cell lysates was detected using anti-Lon antibodies immediately upon HGT (orange) and after the evolutionary experiment (blue) (see Materials and Methods). Strains with IS186 insertion are marked with asterisk. C) Purifying lon knock-out (⊗lon) was performed on naive DHFR-23, 35, 37, and 38 strains (described previously in), and the resulted change in intracellular DHFR abundance in soluble fraction of cell lysates was measured with Western Blot using anti-His antibodies (see Materials and Methods). Abundance of DHFR-35 and 38 changed from an undetected levels to approximately 30% of the WT E. coli DHFR level.
