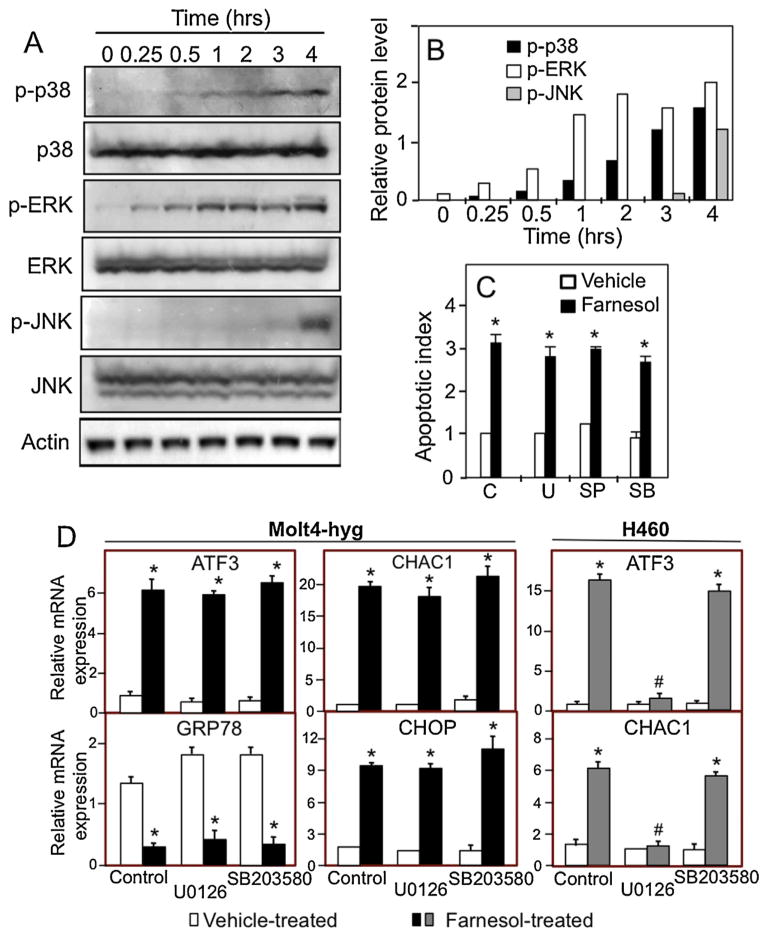
Fig. 7.
Farnesol-induced activation of p38, ERK1/2, and JNK in Molt4-hyg cells. (A) Molt4-hyg cells were treated with 75 μM farnesol. At the time intervals indicated cell lysates were examined by Western blot analysis with antibodies against phosphorylated p38 MAPK (p-p38 MAPK), total p38 MAPK, phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK), total ERK1/2, phosphorylated JNK (p-JNK), and total JNK. (B) The levels of p-p38, p-ERK, and p-JNK shown under A was quantitated and normalized against β-actin as described in Section 2. (C) Molt4-hyg cells were pretreated with vehicle C, p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 (SB, 10 μM), JNK inhibitor SP600125 (SP, 10 μM), or MEK inhibitor U0126 (U, 10 μM) for 30 min and then treated with 75 μM farnesol for 6 h before apoptotic index was determined using a cell death detection ELISA kit. (D) Effect of MEK1/2 and p38 inhibitors on the induction of ATF3, GRP78, CHOP, and CHAC1 in Molt4-hyg and H460 cells. Cells were pretreated with MEK inhibitor U0126 (10 μM) or p38 inhibitor SB203580 (10 μM) for 30 min and then treated with farnesol. After 4 h cells ATF3, GRP78, CHOP, and CHAC1 mRNA expression were evaluated by QRT-PCR as described in Section 2. Each value is the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. *Indicates statistically different from vehicle-treated Molt4-hyg or H460 control (p <0.01).